[Guide] Securely Access IoT Over Internet: Tips & Tricks
Can the promise of the Internet of Things truly be realized without seamless remote control and data retrieval? The ability to securely and efficiently access IoT devices and their data over the internet is not just a technical convenience; it is the very lifeblood of its potential.
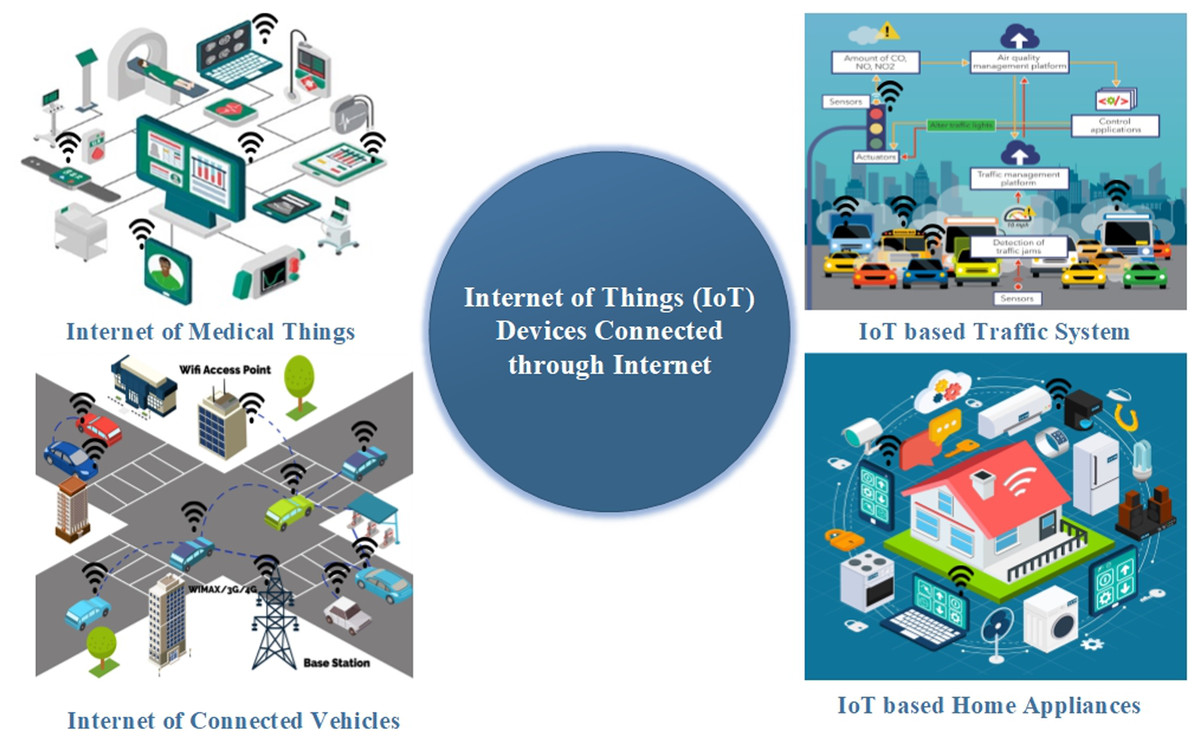
The convergence of ubiquitous connectivity and increasingly sophisticated sensors has given rise to an explosion of Internet of Things (IoT) devices. From smart home appliances and wearable health trackers to industrial machinery and environmental monitoring systems, these connected devices are generating vast amounts of data and offering unprecedented control capabilities. However, the true value of this technology is unlocked only when this data and control can be accessed from anywhere in the world, anytime. This fundamental requirement necessitates robust and secure methods for accessing IoT devices over the internet. The challenges, however, are significant, ranging from ensuring data security and privacy to managing the complexities of device heterogeneity and network infrastructure.
Imagine a scenario: youre away from home, and a sudden storm threatens. You can remotely check the status of your smart home system, verify the integrity of your connected weather sensors, and, if necessary, adjust your heating or cooling system to protect your property. This level of remote access provides a clear and immediate benefit. Consider also the impact on industrial applications: a remote technician can diagnose and repair a piece of equipment on a factory floor thousands of miles away, drastically reducing downtime and associated costs. Or think about a healthcare professional remotely monitoring a patients vital signs, enabling proactive care and potentially preventing a medical emergency. The ability to tap into the data and control offered by the Internet of Things from remote locations is vital to these applications.
The evolution of this capability has moved rapidly. The early days of IoT saw the development of custom solutions for connecting devices to the internet. These frequently involved proprietary protocols and complex configurations. As the field matured, more standardized approaches emerged. The use of open protocols such as MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) and HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) became widespread, allowing devices to communicate with each other and with cloud-based platforms more easily. Cloud computing has become a pivotal component, serving as a central hub for data storage, processing, and analysis, and also for facilitating the secure and scalable remote access to devices.
Security is paramount. Exposing IoT devices directly to the internet can create vulnerabilities. Data breaches and cyberattacks on connected devices pose significant risks, potentially leading to theft of sensitive data, manipulation of devices, or even the disruption of critical infrastructure. Addressing these risks requires a layered approach to security. Encryption plays a key role, protecting data in transit and at rest. Authentication mechanisms verify the identity of users and devices. Authorization controls restrict access to specific resources. Firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular security audits further bolster the security posture.
The architectural landscape of accessing IoT over the internet comprises several key components. First, there are the IoT devices themselves, which can range from tiny sensors and actuators to complex industrial equipment. These devices must be capable of connecting to the internet, typically through Wi-Fi, cellular networks, or wired Ethernet connections. Second, there is a network infrastructure, which provides the communication pathway between the devices and the internet. This infrastructure may include routers, switches, and gateways, as well as cloud service providers. Third, there is an access layer, which provides the means for authorized users to interact with the devices. This layer may include web applications, mobile apps, or APIs (Application Programming Interfaces). Finally, a backend infrastructure, including cloud-based services, facilitates data storage, processing, and analysis, along with the security protocols.
Many organizations are using cloud platforms, for instance, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP), which offer comprehensive IoT services, including device management, data storage, and analytical tools, along with robust security features. These platforms often provide pre-built solutions that simplify the process of connecting, managing, and securing IoT devices. They also offer the scalability and reliability necessary to handle the massive amounts of data generated by IoT devices. However, there are alternatives beyond the big cloud providers, particularly in domains that require more customization, stringent data privacy requirements, or an adherence to local regulations, requiring enterprises to build their own infrastructures. These implementations often involve technologies like VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) and secure gateways.
To offer a better view of the potential implications, consider the work of Dr. Anya Sharma, a leading researcher in the field of remote healthcare monitoring. Her research explores how to make medical devices accessible and safe over the Internet, providing insights for clinicians to deliver proactive care. This example highlights the potential for advancements in remote healthcare and a glimpse into how innovative technologies are changing how people interact with their healthcare providers.
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Full Name | Dr. Anya Sharma |
| Profession | Leading Researcher in Remote Healthcare Monitoring |
| Specialization | Secure IoT in Healthcare, Remote Patient Monitoring |
| Notable Work | Developing secure methods for accessing medical devices remotely; Research on data privacy in healthcare IoT; Publications on predictive analytics in medical devices |
| Affiliations | University Hospital, Department of Biomedical Engineering |
| Key Contributions | Pioneering methods to ensure data security of medical devices accessed over the internet, reducing cyber security risks while maintaining privacy and improving patient care. |
| Areas of Research | Developing robust protocols and infrastructure to enhance secure data access in medical devices and exploring applications that use AI and cloud computing in remote patient monitoring. |
| Website (Example) | Example Medical Research Page |
The rise of edge computing is also reshaping the landscape. Instead of relying solely on cloud-based processing, edge computing moves computational power closer to the devices themselves. This approach reduces latency, conserves bandwidth, and improves the reliability of access, particularly in environments with limited or intermittent internet connectivity. Edge devices can pre-process data, perform real-time analysis, and even make autonomous decisions. This architecture is critical for applications such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and remote healthcare.
Looking ahead, several key trends will further shape the future of accessing IoT over the internet. The rollout of 5G networks is providing ultra-fast and reliable connectivity, enabling more complex and data-intensive IoT applications. The adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) will enhance data analytics, allowing for more intelligent decision-making. Blockchain technology is providing a secure, transparent, and tamper-proof mechanism for managing IoT device identities and data. The increased demand for interoperability standards, which will facilitate communication among different IoT devices and platforms, is of great importance. The development of low-power, wide-area networks (LPWANs) is enabling IoT deployments in areas with poor connectivity, such as rural areas or underground environments.
While the benefits of accessing IoT devices over the internet are undeniable, there are still challenges to overcome. Interoperability remains a hurdle. Different devices and platforms often use different protocols and communication standards, making it difficult to integrate them seamlessly. Data privacy and security continue to be top concerns. As the number of connected devices grows, so does the potential for cyberattacks and data breaches. The cost of implementation and ongoing maintenance can be prohibitive for some organizations, especially small and medium-sized businesses. Regulatory compliance is also a critical concern. The need for adherence to regulations such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) adds complexity and can increase costs.
The future of access IoT over internet will likely be marked by increased automation, heightened security, and greater interoperability. AI and ML will play an increasingly important role in data analysis, enabling predictive maintenance, anomaly detection, and automated decision-making. Advanced security protocols, such as end-to-end encryption and blockchain-based authentication, will become standard. Interoperability standards will evolve, making it easier to integrate different IoT devices and platforms. The growth of edge computing will continue, enabling more real-time processing and decision-making at the edge. As IoT expands, its ability to be accessed and managed over the internet is transforming businesses and lives.
Consider the evolution of agricultural technology. Precision agriculture relies heavily on IoT devices, such as sensors that monitor soil conditions, weather patterns, and crop health. These sensors generate vast amounts of data, which farmers can access remotely via the internet to make informed decisions about irrigation, fertilization, and pest control. This data accessibility has led to increased crop yields, reduced water consumption, and improved efficiency. This is possible because the data is securely transmitted and is accessible whenever and wherever it is needed.
For example, consider a hypothetical company called "AgriTech Solutions." The company specializes in providing IoT solutions to farmers. They deploy soil sensors, weather stations, and crop health monitoring systems across farmlands. Farmers access the data generated by these sensors through a web-based dashboard and a mobile application, allowing them to monitor their fields in real-time, from anywhere with an internet connection. This access enables farmers to optimize their farming practices, leading to higher yields, lower costs, and a more sustainable approach to agriculture. The challenge AgriTech Solutions faced involved creating secure access, integrating disparate sensor data, and ensuring the system's robustness against network failures.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Company Name | AgriTech Solutions |
| Industry | Agricultural Technology (AgTech) |
| Core Services | IoT Solutions for Precision Agriculture, Data Analytics, Remote Monitoring |
| Key Products | Soil Sensors, Weather Stations, Crop Health Monitoring Systems, Web-based Dashboard, Mobile Application |
| Target Audience | Farmers, Agricultural Businesses |
| Value Proposition | Increased crop yields, reduced water consumption, improved efficiency, data-driven decision making. |
| Challenges Faced | Creating secure access, integrating disparate sensor data, ensuring system robustness against network failures. |
| Technologies Used | IoT Sensors, Cloud Computing, Web Technologies, Mobile Development |
| Outcome | Higher yields, lower costs, a more sustainable approach to agriculture. |
The journey of access IoT over the internet is ongoing. While challenges persist, the potential of this technology to improve efficiency, transform industries, and enhance our quality of life is clear. As technology continues to evolve, the focus on interoperability, security, and user-friendliness will become even more critical. The devices, systems, and the internet that connects them, are transforming the landscape, creating a world where connectivity, efficiency, and convenience are commonplace.