How To Easily Manage IoT Devices Behind A Firewall
Are you wrestling with the complexities of securing your Internet of Things (IoT) devices, hidden behind the protective barrier of your firewall? Understanding and effectively managing your IoT devices in this scenario is no longer a luxury but a critical necessity for businesses and individuals alike. The proliferation of interconnected devices, from smart appliances to industrial sensors, has dramatically expanded the attack surface, making it imperative to implement robust security measures.
The challenge, however, lies in the inherent nature of IoT devices: often designed with security as an afterthought, utilizing weak authentication protocols, and lacking the computational power for sophisticated security measures. This vulnerability is compounded when these devices are deployed behind a firewall, which, while offering a layer of protection, can also create management and visibility challenges. Effective management requires a multi-faceted approach, encompassing network segmentation, intrusion detection and prevention, regular vulnerability assessments, and ongoing monitoring. The convergence of these elements is crucial to ensure that your IoT ecosystem remains resilient against potential threats.
The core issue revolves around the visibility and control you have over these devices. A firewall, by its design, restricts traffic flow, but it can't inherently distinguish between legitimate IoT traffic and malicious activity. Moreover, the sheer volume of devices deployed in modern environments, coupled with the diverse communication protocols they employ, makes manual configuration and monitoring impractical. This necessitates automated solutions, coupled with a deep understanding of the network traffic patterns these devices generate. Ignoring these aspects opens the door to significant security breaches, ranging from data theft to complete system compromise.
Let's delve into the essential elements required to effectively "manage IoT devices behind firewall."
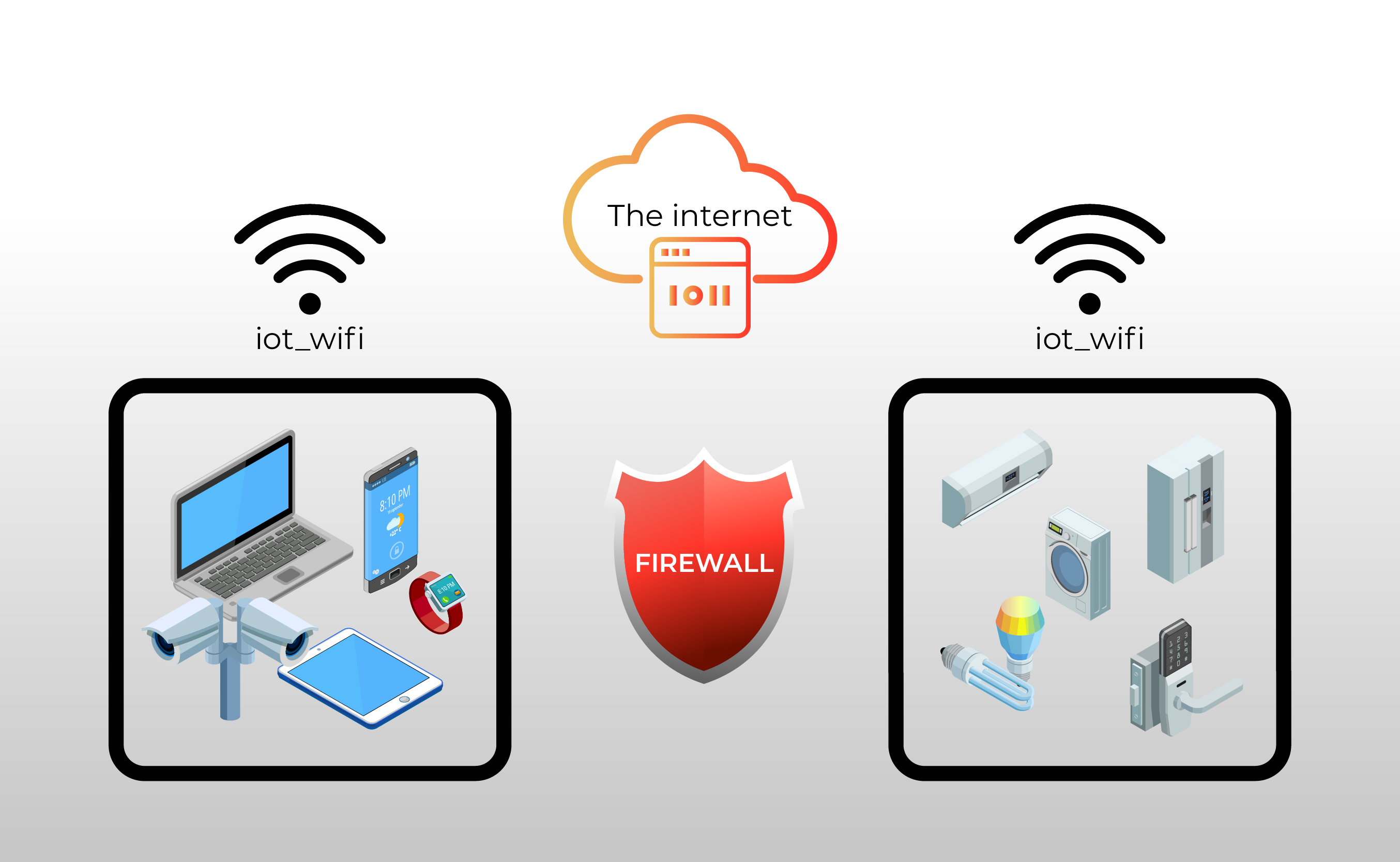
Network Segmentation: One of the most effective strategies is network segmentation. Instead of allowing all IoT devices to reside on the same network as critical business systems, segment them. This involves creating separate VLANs (Virtual LANs) or network segments for IoT devices. By doing so, you limit the potential damage if a device is compromised. A compromised device within a segmented network cannot directly access other critical systems. The firewall then becomes the gatekeeper between these segments, strictly controlling the traffic flow based on pre-defined rules.
For example, imagine you have a network with smart thermostats, security cameras, and industrial sensors. You would create a dedicated VLAN for each type of device, with the firewall controlling what traffic can pass between these VLANs. This segmentation helps to isolate potential threats, reducing the risk of lateral movement within your network. Moreover, it simplifies the application of security policies tailored to each device type. For instance, you can enforce stricter access control for security cameras compared to the smart thermostats. This focused approach enhances your overall security posture.
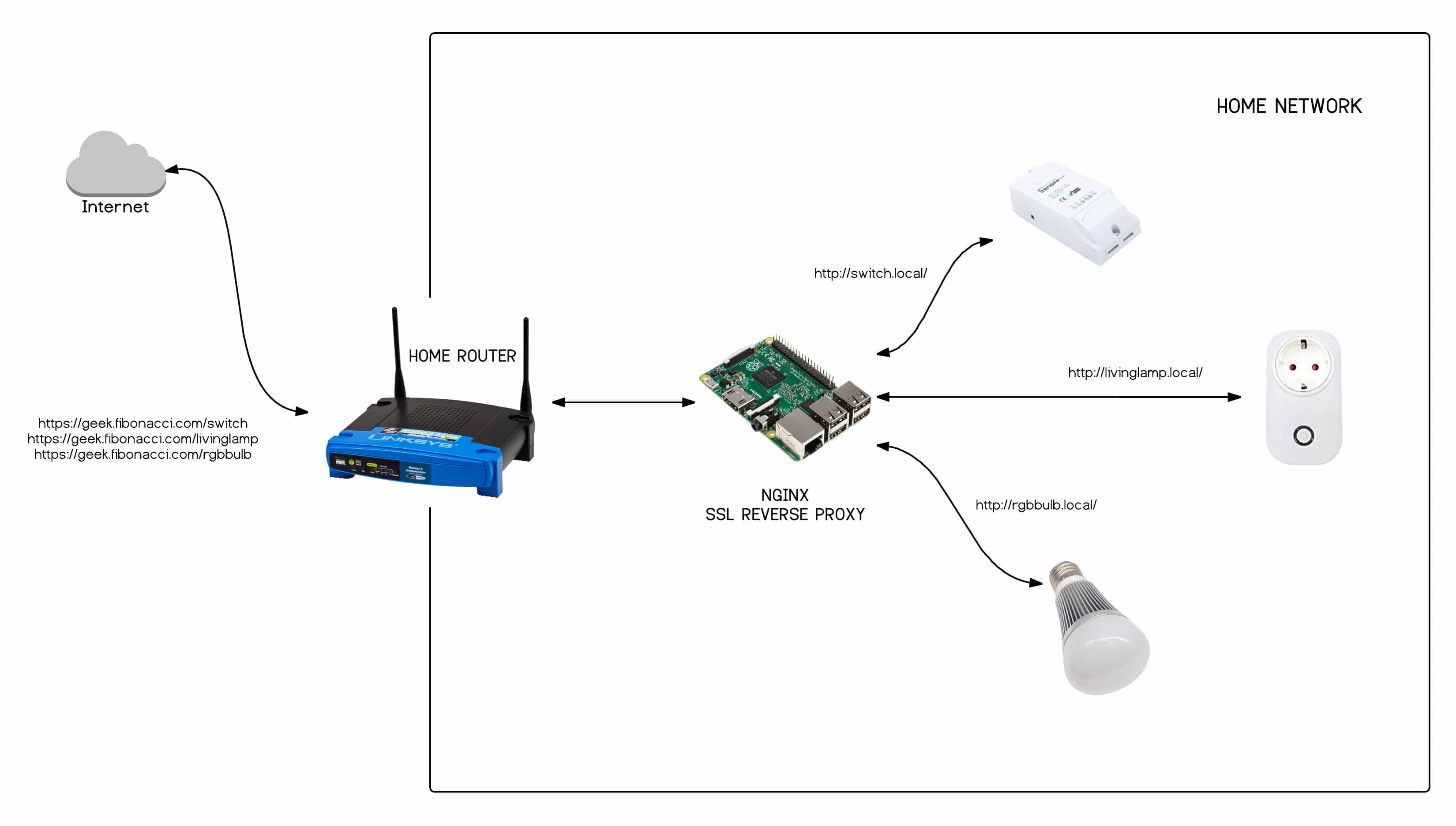
Firewall Configuration and Rules: Your firewall configuration is the linchpin of your IoT security strategy. The firewall rules should be meticulously crafted to permit only the necessary traffic to and from your IoT devices. Default-deny policies are highly recommended: block all traffic by default and only allow specific traffic based on defined rules. This approach minimizes the attack surface, limiting the exposure of your IoT devices. Define clear traffic rules for each type of IoT device, specifying the source and destination IPs, ports, and protocols allowed. Regularly review and update these rules to adapt to changes in your IoT device ecosystem and evolving threat landscape.
When configuring your firewall, consider the communication patterns of your IoT devices. Many IoT devices communicate with cloud services or remote servers. Ensure your firewall rules allow outbound traffic to these necessary destinations, while blocking any unnecessary outbound connections. Enable logging and monitoring capabilities on your firewall to track all traffic, including IoT traffic. This will provide valuable insights into network activity and potential anomalies. Tools like intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS) can further enhance the effectiveness of your firewall by detecting and blocking suspicious activities.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): Implementing an IDPS is crucial for detecting and preventing malicious activities targeting your IoT devices. IDPS solutions monitor network traffic for suspicious patterns, such as unauthorized access attempts, unusual data transfers, or attempts to exploit known vulnerabilities. When a threat is detected, the IDPS can automatically block the malicious traffic or alert security personnel.
Choose an IDPS solution that is specifically designed to monitor IoT traffic, and understand the unique characteristics of your IoT devices. The IDPS must be able to understand the protocols used by your IoT devices. Configure the IDPS to scan for common IoT vulnerabilities, such as weak passwords, unencrypted communication, and known software flaws. IDPS can automatically generate alerts for suspected malicious activity. Regularly update the IDPS with the latest threat intelligence to ensure it can detect new and emerging threats.
Vulnerability Assessment and Patch Management: Regular vulnerability assessments are essential for identifying weaknesses in your IoT devices and your network. Conduct these assessments on a regular basis to identify any known vulnerabilities. These assessments will identify the vulnerabilities in the operating systems and firmware of your IoT devices. Once identified, these vulnerabilities need to be addressed promptly. Develop a patch management strategy for your IoT devices. This involves identifying and applying security patches to the devices' firmware and software. Establish a process for testing patches before deploying them to your production devices to ensure compatibility and avoid disruptions.
In some cases, it may not be possible to directly patch the IoT devices. If the device does not support patching, or if patches are not available, consider alternative mitigation strategies such as network segmentation and access control. Regularly review your vulnerability assessment reports and prioritize addressing high-risk vulnerabilities. Automated vulnerability scanning tools can streamline the vulnerability assessment process.
Endpoint Security: Endpoint security solutions are essential for protecting IoT devices. Endpoint security can prevent the execution of malicious code. Implement strong authentication mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access. Many IoT devices come with default credentials. Change the default credentials to strong, unique passwords. Regularly monitor the devices for any signs of compromise and deploy endpoint detection and response (EDR) capabilities to detect and respond to advanced threats. Ensure that all IoT devices are using secure communication protocols. Use encryption to protect sensitive data in transit.
Monitoring and Logging: Implement comprehensive monitoring and logging for your IoT devices. Collect logs from all IoT devices and your network infrastructure to track activity. Regularly review these logs to identify any anomalies or suspicious activities. Utilize security information and event management (SIEM) systems to centralize your logging and monitoring. These systems can correlate data from various sources to provide a holistic view of your security posture. Configure alerts to notify security personnel of any suspicious events.
Regular Security Audits: Conducting regular security audits is essential for evaluating the effectiveness of your IoT security measures. Security audits can identify any weaknesses in your IoT security posture and make recommendations for improvements. The audits need to be conducted by both internal and external security professionals. These audits should encompass all aspects of your IoT security strategy, including network segmentation, firewall configuration, vulnerability assessment, and incident response. The audit results provide critical insights into your security posture and help you identify areas for improvement.
Incident Response Plan: Even with the best security measures in place, security incidents can still occur. Develop a well-defined incident response plan for your IoT devices. This plan should outline the steps to take in the event of a security breach. This includes steps for identification, containment, eradication, and recovery. Regularly test your incident response plan to ensure its effectiveness. Train your security personnel to respond effectively to security incidents and establish a communication plan to inform relevant stakeholders.
Secure Firmware and Software Updates: The security of IoT devices depends heavily on the trustworthiness of their firmware and software. Establish a secure update process to ensure that you only install trusted firmware and software updates. Verify the authenticity of the updates by verifying their digital signatures and implementing a rollback mechanism to revert to a previous version of the firmware if the update fails. Always install the latest firmware updates on your IoT devices to address security vulnerabilities.
Supply Chain Security: The security of your IoT devices starts at the supply chain. Evaluate the security practices of your IoT device vendors. Ensure they have a strong commitment to security and follow secure development practices. Scrutinize the manufacturers, as well as their security practices. This will help you to make informed decisions about the vendors you choose. Require that vendors adhere to security standards and best practices.
Physical Security: Don't forget about physical security. Consider the physical security of your IoT devices and protect them from unauthorized access or tampering. Restrict physical access to IoT devices. Place the devices in secure locations. In the case of industrial IoT devices, ensure they are housed in secure, locked cabinets, and implement physical access controls to prevent tampering. Implement measures to protect your IoT devices from theft or damage.
Education and Training: Your employees play a critical role in your IoT security. Provide regular security awareness training to all employees to educate them about the risks associated with IoT devices and how to protect themselves. Educate your staff about best practices for IoT security, such as strong passwords and recognizing phishing attempts. By improving security awareness, you reduce the likelihood of human error leading to a security breach.
Compliance and Regulations: Be aware of and comply with all relevant regulations and industry standards. Many industries have specific security standards and regulations for IoT devices. Ensure your IoT security strategy aligns with those regulations. This may include, for example, specific compliance requirements for data security and privacy. Regularly audit your IoT security practices to ensure compliance and make sure you adhere to regulations applicable to your industry.
The Future of IoT Security: The landscape of IoT security is constantly evolving, with new threats and vulnerabilities emerging regularly. Stay informed about the latest security threats and vulnerabilities. The Internet of Things is an ever-evolving landscape. Embrace a proactive approach to security, adopting the most recent security solutions, and continuously improving your security posture.
Conclusion: Managing IoT devices behind a firewall is a complex undertaking, but the rewards of a secure IoT environment are substantial. By implementing a comprehensive security strategy that encompasses network segmentation, firewall configuration, IDPS, vulnerability assessments, endpoint security, monitoring, and incident response, you can significantly reduce the risks associated with your IoT devices and protect your valuable data and assets. This demands a commitment to ongoing monitoring, continuous improvement, and a proactive approach to emerging threats. Only then can you ensure the long-term security and integrity of your connected devices and the data they generate.