How To Remotely Control IoT Devices: A Beginner's Guide
Can you imagine a world where your home adapts to your every need, where your devices anticipate your desires, and where you can orchestrate your digital life from anywhere on Earth? The power to control IoT devices remotely is rapidly transforming from a futuristic concept into a tangible reality, reshaping how we interact with our environment and offering unprecedented levels of convenience and control. The implications of this technological revolution are profound, extending from the mundane to the extraordinary, and touching nearly every facet of modern existence.
The ability to control IoT devices remotely is more than just a technological marvel; it's a fundamental shift in how we perceive and interact with our surroundings. Consider the simple act of adjusting your thermostat before you arrive home on a frigid winter evening, or checking on your security cameras while you are miles away on vacation. These are just glimpses of the potential that remote IoT control unlocks, offering a sense of freedom, security, and efficiency previously unimaginable. From smart homes and connected cars to industrial automation and healthcare monitoring, the ability to manage and monitor devices from afar is driving innovation and creating new possibilities across a wide spectrum of industries.
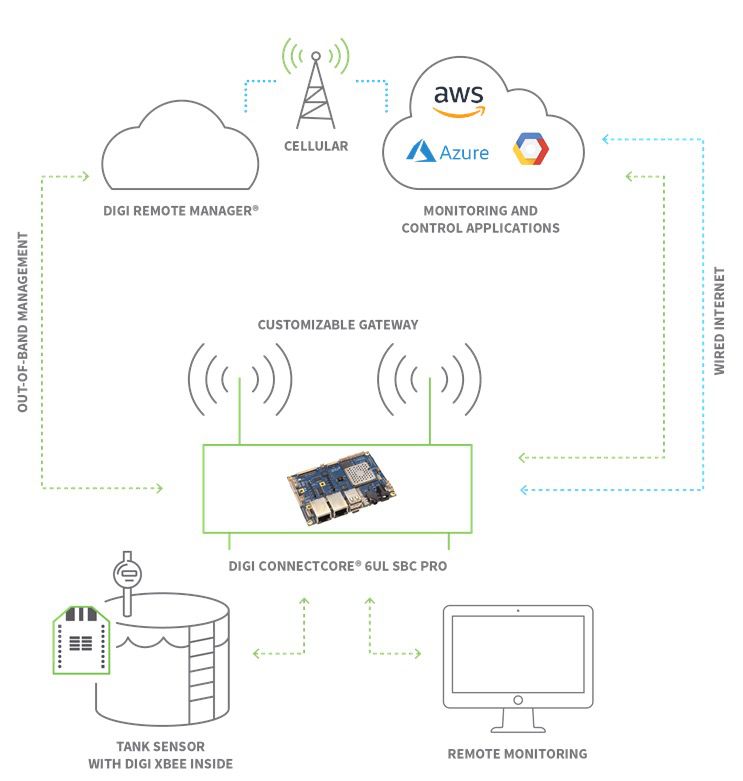
Let's delve into the intricate details of how "control IoT device remotely" works, examining its various applications and the technologies that make it possible. Remote control of IoT devices relies on several key components: the devices themselves, the communication protocols, and the control interface. IoT devices, such as smart appliances, sensors, and actuators, are equipped with embedded systems that enable them to connect to the internet. These devices are designed to communicate with a central control system or a user interface, using a variety of communication protocols. Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, and cellular networks are some of the common protocols employed in IoT device communication, each offering unique advantages in terms of range, speed, and power consumption. The control interface can be a smartphone app, a web-based dashboard, or even voice assistants like Amazon Alexa or Google Assistant. This interface allows users to send commands to the IoT devices, monitor their status, and receive data from them.
The architecture for remote control is diverse, often tailored to the specific application and the devices involved. In a smart home, for instance, a central hub might act as the control point, managing communication with various devices like smart lights, thermostats, and security systems. This hub then connects to the internet, enabling users to control the devices remotely through a mobile app or a web interface. In industrial settings, remote control systems are often more complex, involving specialized gateways and protocols to manage a large number of devices and ensure secure communication.
Security considerations are paramount when implementing remote control systems. IoT devices are often vulnerable to cyberattacks, and unauthorized access can have serious consequences, from data breaches to physical damage. Strong authentication methods, encryption, and regular security updates are essential to protect IoT devices and the data they collect. The use of virtual private networks (VPNs) and firewalls further enhances security by creating a secure tunnel for communication and preventing unauthorized access.
The applications of remote IoT device control are incredibly diverse, spanning numerous sectors and improving efficiency and convenience in ways we've only just begun to explore. In the realm of smart homes, remote control enables homeowners to manage lighting, climate control, security systems, and entertainment systems from anywhere in the world. Imagine being able to preheat your oven while you are on your way home from work, or adjust your thermostat to conserve energy when you are away on vacation. Smart appliances like refrigerators, washing machines, and dishwashers can be monitored and controlled remotely, providing valuable insights into their performance and allowing for proactive maintenance.
In the industrial sector, remote control is transforming manufacturing, logistics, and energy management. Remote monitoring and control of machinery can improve efficiency and reduce downtime by allowing operators to diagnose and resolve issues from a remote location. Automated systems can be controlled remotely to optimize production processes, reduce energy consumption, and ensure worker safety. In the field of healthcare, remote patient monitoring allows healthcare providers to monitor patients' vital signs, administer medications, and provide telehealth services from a distance. This is particularly useful for patients with chronic conditions, those living in remote areas, or those who require frequent monitoring.
Another key area benefiting from remote IoT control is transportation. Connected cars can be controlled remotely for various purposes, such as starting the engine, locking and unlocking doors, and tracking the vehicle's location. This is useful in case of emergencies and also allows for convenient features like remote climate control. Furthermore, remote control plays a significant role in fleet management, enabling companies to monitor the location, performance, and maintenance needs of their vehicles. Drones, another application of remote control, are used for a variety of purposes, including delivery services, surveillance, and agricultural monitoring.
The rapid proliferation of IoT devices and the increasing demand for remote control capabilities have created a burgeoning market for related products and services. The smart home market is booming, with consumers increasingly embracing connected devices to enhance their lifestyles. Smart thermostats, security systems, and lighting controls are becoming commonplace, and the market for these devices is expected to continue growing. The industrial IoT market is also experiencing rapid growth, driven by the increasing adoption of automation and remote monitoring technologies in manufacturing, logistics, and other industries. Companies are investing in platforms and solutions that enable them to collect and analyze data from their devices, optimize their operations, and improve their bottom line.
The future of "control IoT device remotely" is bright, with exciting developments on the horizon. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) will enhance the capabilities of remote control systems, enabling them to make intelligent decisions and automate tasks. For example, AI-powered smart homes could learn a user's habits and preferences, automatically adjusting the lighting, temperature, and other settings to optimize comfort and energy efficiency. The development of 5G networks will further improve the speed and reliability of remote communication, enabling new applications and improving the performance of existing ones. 5G's low latency and high bandwidth will be particularly beneficial for applications that require real-time control, such as autonomous vehicles and remote surgery.
Blockchain technology has the potential to enhance the security and transparency of remote IoT control systems. Blockchain can be used to create secure and tamper-proof records of device activity, making it more difficult for attackers to compromise the system. Quantum computing, though still in its early stages of development, has the potential to revolutionize remote control systems by enabling faster and more efficient processing of large datasets. Quantum computers could be used to optimize complex algorithms, analyze vast amounts of data, and develop new AI-powered solutions.
The journey towards fully realizing the potential of "control IoT device remotely" is not without challenges. Interoperability, security, and user privacy are some of the key challenges that must be addressed to ensure the widespread adoption of this technology. Interoperability refers to the ability of different devices and systems to communicate and work together seamlessly. Currently, the IoT landscape is fragmented, with many devices using proprietary protocols and communication standards. Addressing this challenge requires the development and adoption of open standards that enable different devices to communicate and interact with each other.
Security is another major concern. As IoT devices become more prevalent, they become increasingly vulnerable to cyberattacks. Ensuring the security of these devices and protecting the data they collect is essential to maintaining user trust and preventing malicious actors from compromising the systems. This requires a multi-layered approach to security, including strong authentication methods, encryption, regular security updates, and the implementation of security best practices.
User privacy is also a significant concern. IoT devices often collect a large amount of personal data, raising concerns about how that data is being used and protected. Ensuring the privacy of user data requires the implementation of strict data privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), and the adoption of privacy-enhancing technologies. Transparency about data collection practices and the ability for users to control their data are essential to building trust and protecting user privacy.
Looking forward, "control IoT device remotely" will continue to evolve, driven by technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and the increasing demand for automation and control. We can expect to see more sophisticated and intuitive user interfaces, enhanced security features, and the integration of AI and ML to create intelligent and responsive systems. The expansion of 5G networks will further accelerate the adoption of remote control technologies, enabling new applications and improving the performance of existing ones.
Furthermore, we can expect to see greater collaboration between technology providers, policymakers, and industry stakeholders to address the challenges of interoperability, security, and user privacy. The development of open standards, robust security protocols, and comprehensive data privacy regulations will be crucial to ensuring the widespread adoption of "control IoT device remotely" and realizing its full potential.
In conclusion, "control IoT device remotely" is a transformative technology that is reshaping how we interact with our environment and offering unprecedented levels of convenience, efficiency, and control. From smart homes and connected cars to industrial automation and healthcare monitoring, remote control is driving innovation and creating new possibilities across a wide spectrum of industries. While challenges remain in terms of interoperability, security, and user privacy, the future of remote IoT control is bright, with exciting developments on the horizon. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more sophisticated, intuitive, and secure remote control systems that will further enhance our lives and transform the way we work and play. It is a technology that is not just about controlling devices, but about shaping a future where technology seamlessly integrates into our lives, offering us more control, more convenience, and a greater sense of freedom.