Securing IoT Devices: A Guide To Firewalls & Best Practices
In an era where interconnected devices permeate every facet of life, from the mundane to the mission-critical, how do we safeguard this burgeoning ecosystem of the Internet of Things (IoT) against the ever-evolving threats of the digital landscape? The answer lies in a proactive and multifaceted approach, emphasizing robust security measures, intelligent network segmentation, and a keen understanding of the inherent vulnerabilities within these devices.
The Internet of Things, often abbreviated as IoT, represents a paradigm shift in how we interact with technology. It signifies the vast network of physical deviceseverything from smart refrigerators and wearable health monitors to industrial sensors and sophisticated automation systemsembedded with sensors, software, and other technologies that enable them to connect and exchange data over the internet. This connectivity, while offering unprecedented convenience and efficiency, also introduces a complex web of security challenges that must be addressed with meticulous care. Whether it's a smart home, an industrial IoT setup, or a sprawling corporate network, securing these devices demands a nuanced understanding of the threats and a strategic implementation of best practices.
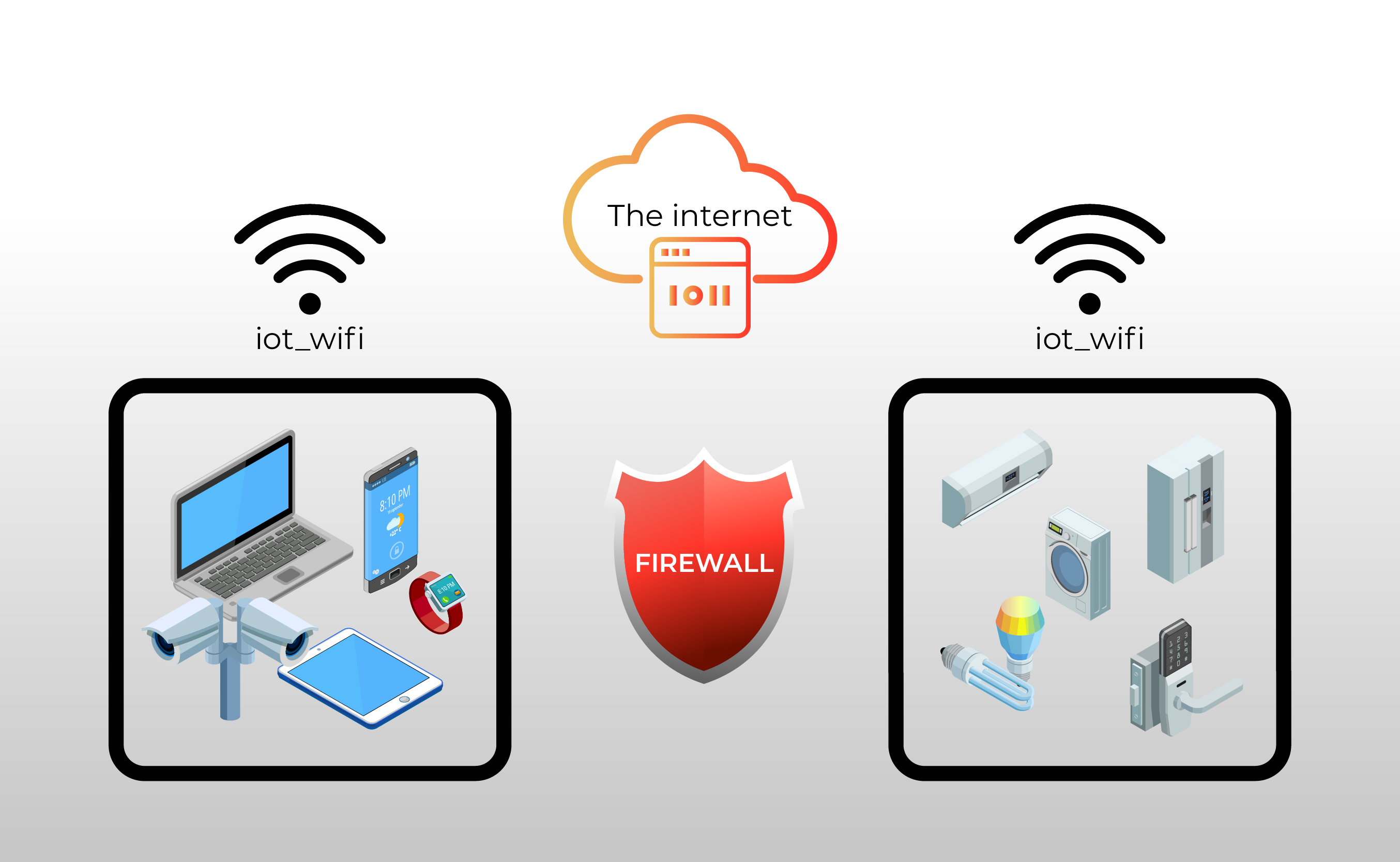
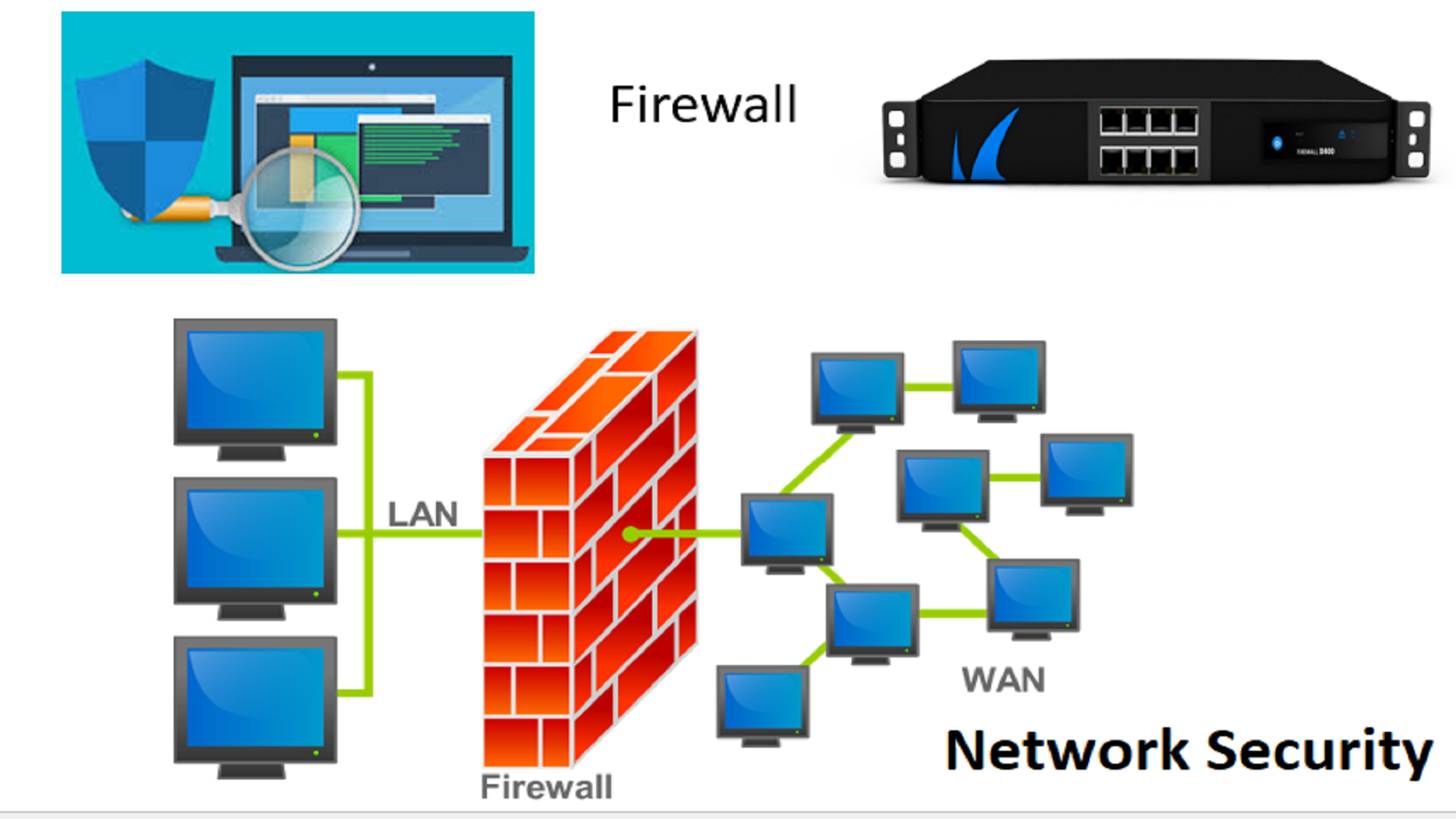
The core of effective IoT security rests on a multi-layered defense strategy. Firewalls, acting as digital gatekeepers, play a pivotal role. However, they are not a panacea. Deploying a firewall to protect an IoT network is not as simple as installing the hardware. Therefore, configuring and optimizing firewalls specifically for IoT devices is essential, as improper settings can impede device functionality. This article dives deep into the intricacies of managing IoT devices behind a firewall, offering practical examples, actionable insights, and expert advice to provide a deep understanding of the challenges involved.
Furthermore, managing IoT devices behind firewalls introduces an additional layer of complexity, as firewalls, designed to protect networks from unauthorized access, can also unintentionally hinder remote access to IoT devices. Finding a balance between security and accessibility is thus a crucial endeavor.
Remote access to IoT devices is often necessary for maintenance, updates, and troubleshooting, but this also introduces attack vectors that must be carefully managed. Solutions such as "remoteiot" have become essential tools for secure and reliable connectivity. Using remoteiot behind a firewall, however, presents unique challenges. This guide will walk you through setting up and using remoteiot in such situations, providing detailed guidance and practical examples.
As the IoT ecosystem grows, the need for secure device management has become more critical. The proliferation of interconnected devices has introduced new vulnerabilities, making it imperative to implement robust security measures. This includes strategies such as isolating IoT devices from other critical business systems. One practical approach is to manage IoT devices behind a firewall using Ubuntu as the operating system, known for its robust security features and versatility. Segmentation of the network is critical, and firewalls can help isolate smart home devices from critical business systems.
Another crucial aspect of IoT management is compliance with industry-specific regulations and standards. Many industries and jurisdictions have implemented mandates regarding data privacy, security, and network configurations. Failure to meet these requirements can result in substantial fines and legal ramifications. By carefully managing IoT devices behind firewalls and implementing comprehensive security measures, organizations can significantly improve their compliance posture.
To provide a comprehensive overview of the technologies and strategies involved in IoT security, let's look at a consolidated view of the key aspects:
Best practices for managing IoT devices are designed to secure and maintain these devices. Following these practices helps organizations to create a secure and efficient environment for their IoT devices.
Managing remote IoT setups behind firewalls requires a strategic approach, integrating network segmentation, secure protocols, and ongoing monitoring to maintain both operational efficiency and data security. It's about providing a balance between security and accessibility. Remote access solutions can be a gateway to these secure connectivity solutions.
Understanding IoT and its challenges is the first step towards effective management and security. This includes identifying the various types of IoT devices, understanding the vulnerabilities associated with each, and recognizing the specific threats that organizations or individuals face.
In addition to firewalls, there are other tools and technologies to consider. These range from intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS) to vulnerability scanners and endpoint security solutions. Data security in IoT management is paramount, especially when dealing with sensitive information.
As the landscape evolves, firewalls are becoming more sophisticated. The future of IoT and firewall management will see increased automation, AI-powered threat detection, and more seamless integration with cloud platforms. It is critical to adapt and stay ahead of the curve.
For a more detailed look at the best practices, key technologies, and future of IoT and firewall management, lets create a table for a comprehensive overview of the topic:
| Category | Description | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| What is IoT and Why it Matters | The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of physical devices embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies that enable them to connect and exchange data over the internet. | Understanding device types, data flow, and potential vulnerabilities. |
| Securing IoT Devices in an Enterprise Environment | Establishing robust security measures to protect interconnected devices from cyber threats. | Network segmentation, firewall configuration, access control, regular security audits. |
| Best Practices for Managing IoT Devices | Implementing proven strategies to ensure the secure and efficient operation of IoT devices. | Regular firmware updates, strong passwords, encryption, and monitoring. |
| Tools and Technologies to Consider | Exploring the various tools and technologies available for securing and managing IoT devices. | Firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS/IPS), vulnerability scanners, and endpoint security solutions. |
| Data Security in IoT Management | Prioritizing the security and privacy of data collected and transmitted by IoT devices. | Data encryption, access control, data anonymization, compliance with privacy regulations. |
| How to Manage IoT Behind a Firewall | Configuring and optimizing firewalls to protect IoT devices while allowing necessary access. | Proper firewall rules, port management, and network segmentation. |
| Remote IoT Solutions | Using remote solutions for secure IoT devices to ensure reliable and secure connectivity. | Selecting secure protocols (e.g., VPN), secure configuration of the remote access, and monitoring traffic. |
| Advanced Techniques for IoT Security | Implementing advanced security measures to protect IoT devices. | Threat intelligence, behavioral analysis, and zero-trust security models. |
| The Future of IoT Device and Firewall Management | Examining emerging trends and technologies that will shape the future of IoT device management. | AI-powered threat detection, automation, and cloud-based management. |
| Compliance | Meeting industry standards and regulatory requirements to ensure data privacy and security. | Adhering to HIPAA, GDPR, and other relevant regulations. |
Managing IoT devices securely is not merely a technical challenge but a critical imperative in an increasingly interconnected world. By embracing a proactive security posture, organizations and individuals can successfully navigate the complexities of IoT, ensuring both operational efficiency and the protection of sensitive data. The key lies in understanding the potential vulnerabilities, implementing a layered defense strategy, and staying abreast of the ever-evolving landscape of threats and technologies.