[Guide] Effortlessly Control IoT Devices Over Internet - 2024
Can everyday objects truly be controlled from anywhere in the world? The answer, increasingly, is a resounding yes, a transformation driven by the ability to control IoT devices over the internet. This seemingly simple concept is reshaping industries, redefining convenience, and ushering in an era of unprecedented connectivity.
The ability to command devices remotely, whether a thermostat, a security system, or a complex piece of industrial machinery, hinges on the convergence of several key technologies. At its core, its about the seamless integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices with the internet itself. This allows devices to receive instructions and transmit data, enabling real-time control and monitoring. The impact of this technological leap is far-reaching, extending from smart homes to sprawling industrial complexes, and the possibilities are only beginning to be explored. What began as a novelty is quickly becoming a necessity.
Let's delve into a scenario that underscores this shift. Consider a homeowner, Sarah, who is on vacation. She can adjust the thermostat from her smartphone, ensuring her house is the perfect temperature upon her return, saving energy and money. If a security alarm is triggered, she can view the security camera feeds immediately and alert the authorities if necessary. The same technology allows a farmer to monitor soil conditions in real time and adjust irrigation systems remotely, boosting crop yields and conserving water. A factory manager can monitor and control machinery from a central control room, improving efficiency and reducing downtime. The implications are endless.
This technology, though seemingly simple, has complexities that are not always apparent. The core component is the IoT device itself. These devices are usually small and designed to collect data and perform a task. The IoT devices must have a network connection, typically through Wi-Fi, cellular, or a proprietary wireless protocol. This connection enables the device to communicate with the internet. Cloud platforms provide the infrastructure for storing and processing the data generated by IoT devices. They also offer the tools needed to control the devices remotely. Finally, the user interface, which can be a smartphone app, a web portal, or a dashboard, provides the means for the user to interact with the system.
A critical aspect often overlooked is security. Because IoT devices are connected to the internet, they are vulnerable to cyberattacks. Securing these devices is therefore paramount. Strong password policies, encryption, and regular software updates are vital to protect against unauthorized access. This includes protecting the data that these devices collect. End-to-end encryption, secure data storage, and compliance with privacy regulations such as GDPR are essential to maintaining user trust and ensuring the responsible use of this powerful technology. Furthermore, the concept of interoperability is also crucial. IoT devices from different manufacturers must be able to communicate with each other and work seamlessly together. This requires the adoption of open standards and protocols.
To understand the scope and breadth of "control IoT device over internet," we can start by looking at several key use cases: smart homes, industrial automation, healthcare, transportation, and agriculture. In smart homes, homeowners can remotely control lighting, climate control, security systems, and appliances. In industrial automation, manufacturers can monitor and control equipment, optimizing production processes and reducing downtime. In healthcare, remote patient monitoring and connected medical devices are enabling better patient care and outcomes. In transportation, connected vehicles can share data and improve safety and efficiency. And in agriculture, farmers can remotely monitor and control irrigation systems, monitor crop health, and optimize resource use.
Consider the smart home environment. The benefits are multifaceted. Convenience is increased. Homeowners can control various aspects of their home from anywhere in the world, which gives them a sense of security. Energy efficiency is improved as systems can be automated to conserve energy. In the realm of security, integrated security systems can be managed remotely, which provides immediate responses to any potential security breaches. But the potential issues also need consideration: security vulnerabilities, lack of standardization, and the potential for privacy breaches.
Industrial automation, on the other hand, uses similar technology but at a larger scale. It transforms manufacturing and operational processes. The advantages are significant. Greater operational efficiency, as remote monitoring allows for real-time performance data collection and instant responses. Reduced downtime, which leads to cost savings and improved productivity. Data-driven decision-making. But the potential downsides cannot be ignored: cybersecurity risks, the complexity of implementation, and the initial costs involved.
The use of "control IoT device over internet" in healthcare has far-reaching implications. Remote patient monitoring makes it possible to monitor patients from their homes, which improves access to care and reduces hospital readmissions. Connected medical devices such as implanted sensors can collect real-time data, which helps improve diagnostics. The downsides are not to be ignored. Security and privacy risks, the need for extensive data management, and regulatory hurdles are all factors to consider.
The rise of connected vehicles has created an environment where "control IoT device over internet" is also relevant. Connected vehicles can share data, which improves safety and enables more efficient traffic management. The vehicle owner can gain access to real-time data, which helps to optimize the driving experience. The challenges are significant. Cybersecurity risks, privacy concerns, and the need for robust infrastructure development are concerns that should be addressed.
In the realm of agriculture, "control IoT device over internet" offers the possibility of more efficient farming. Remote monitoring of irrigation systems and soil conditions allows for optimized resource usage, which leads to higher yields and lower costs. Real-time monitoring of crop health, allows for early detection and management of diseases and pests. Data-driven decision-making is facilitated. But there are difficulties. The complexity of implementation, cybersecurity risks, and the need for reliable connectivity in rural areas are all to be accounted for.
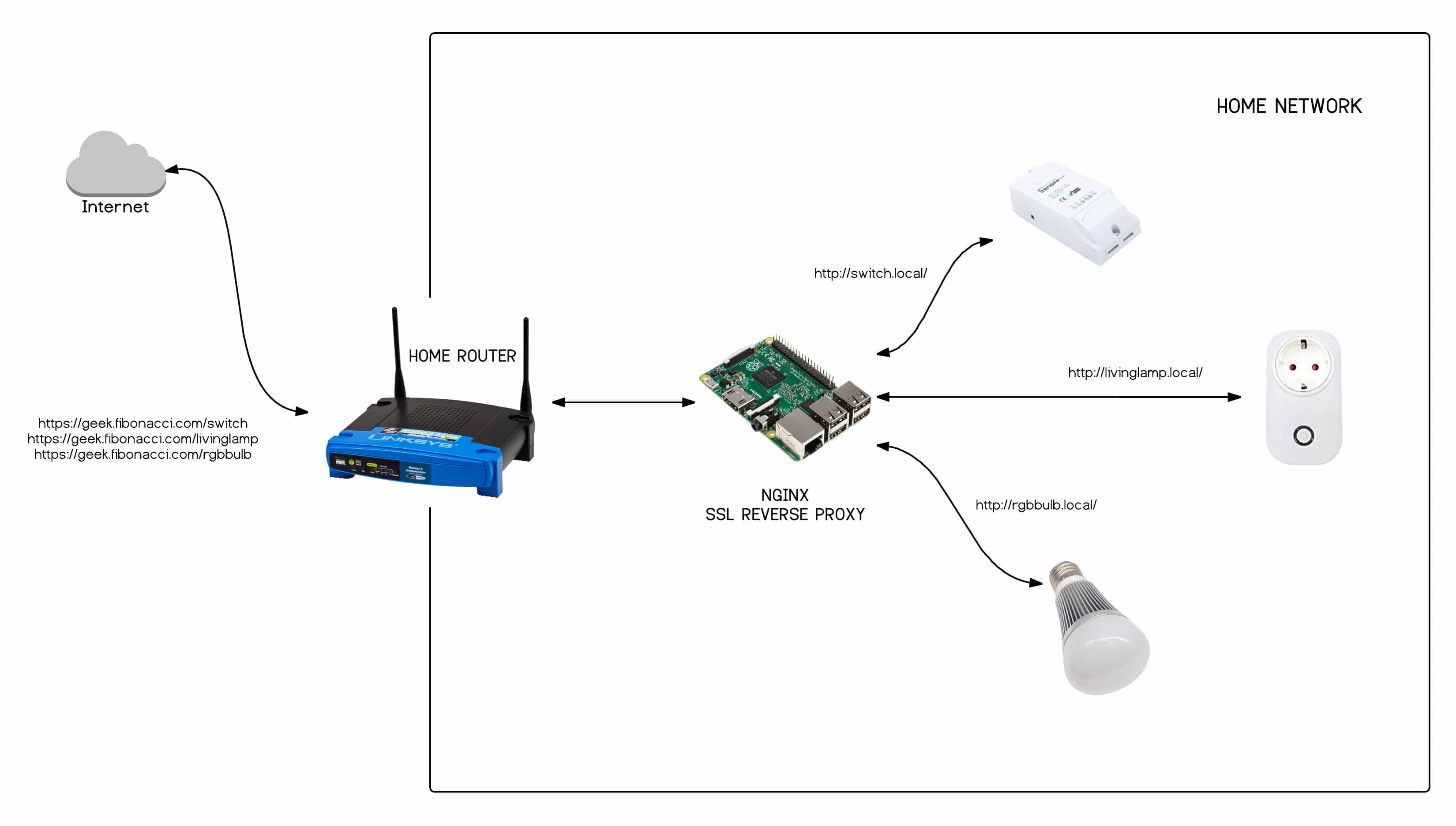
The architecture that underpins the "control IoT device over internet" functionality is built on several layers. At the very bottom is the hardware layer, which consists of the physical devices themselves: sensors, actuators, and gateways. These devices collect data, perform actions, and connect to the network. The network layer then facilitates communication between the devices and the cloud platform. This includes protocols such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular networks. The cloud platform provides the infrastructure for storing, processing, and managing the data generated by the devices. It also provides the tools needed to control the devices remotely. Finally, the application layer provides the user interface and the applications that allow users to interact with the system.
The future of "control IoT device over internet" is promising. The development of new technologies, such as 5G and edge computing, will further enhance the capabilities of IoT devices. 5G networks will provide faster and more reliable connectivity, while edge computing will allow for data processing and analysis closer to the devices, which reduces latency and improves performance. Artificial intelligence and machine learning will play a key role in optimizing the performance of IoT devices. The use of these technologies to automate decision-making and enable predictive maintenance, is also on the horizon. However, ethical considerations and the need for greater standardization and security are still issues to be addressed.
As "control IoT device over internet" becomes ever more prevalent, the importance of establishing strong security measures cannot be overemphasized. Strong passwords and multi-factor authentication are foundational. Encryption is critical. Software updates must be implemented regularly. The focus on securing the entire IoT ecosystem is paramount. Data privacy regulations such as GDPR and CCPA need to be followed. The need for industry-wide cooperation in establishing security standards and best practices is essential.
The trend of "control IoT device over internet" is rapidly expanding. The possibilities are extensive, which cover an array of industries. This technology is reshaping the world. A responsible approach to development is crucial to fully realize the potential of this transformative technology.