Top Remote Access IoT Examples & How They Work
Is the Internet of Things (IoT) truly living up to its transformative potential, or are we merely scratching the surface? Remote access, a cornerstone of the IoT revolution, is the key that unlocks unparalleled possibilities, allowing us to control, monitor, and manage devices from virtually anywhere.
The allure of the IoT lies in its promise of seamless connectivity and intelligent automation. At its heart, this means the ability to interact with devices remotely. Remote access, in this context, transcends simple commands; it's about gathering real-time data, troubleshooting issues, and implementing updates without the need for physical presence. This capability has redefined industries, from manufacturing and healthcare to agriculture and smart homes. It has changed the paradigm for how we interact with technology, shifting from a localized experience to a globally connected ecosystem.
To understand the breadth of remote access IoT examples, it's useful to break down the concept. At its core, remote access allows for the manipulation and observation of devices over a network, most commonly the internet. This can be achieved through a variety of technologies, including Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), Secure Shell (SSH) connections, and dedicated IoT platforms.
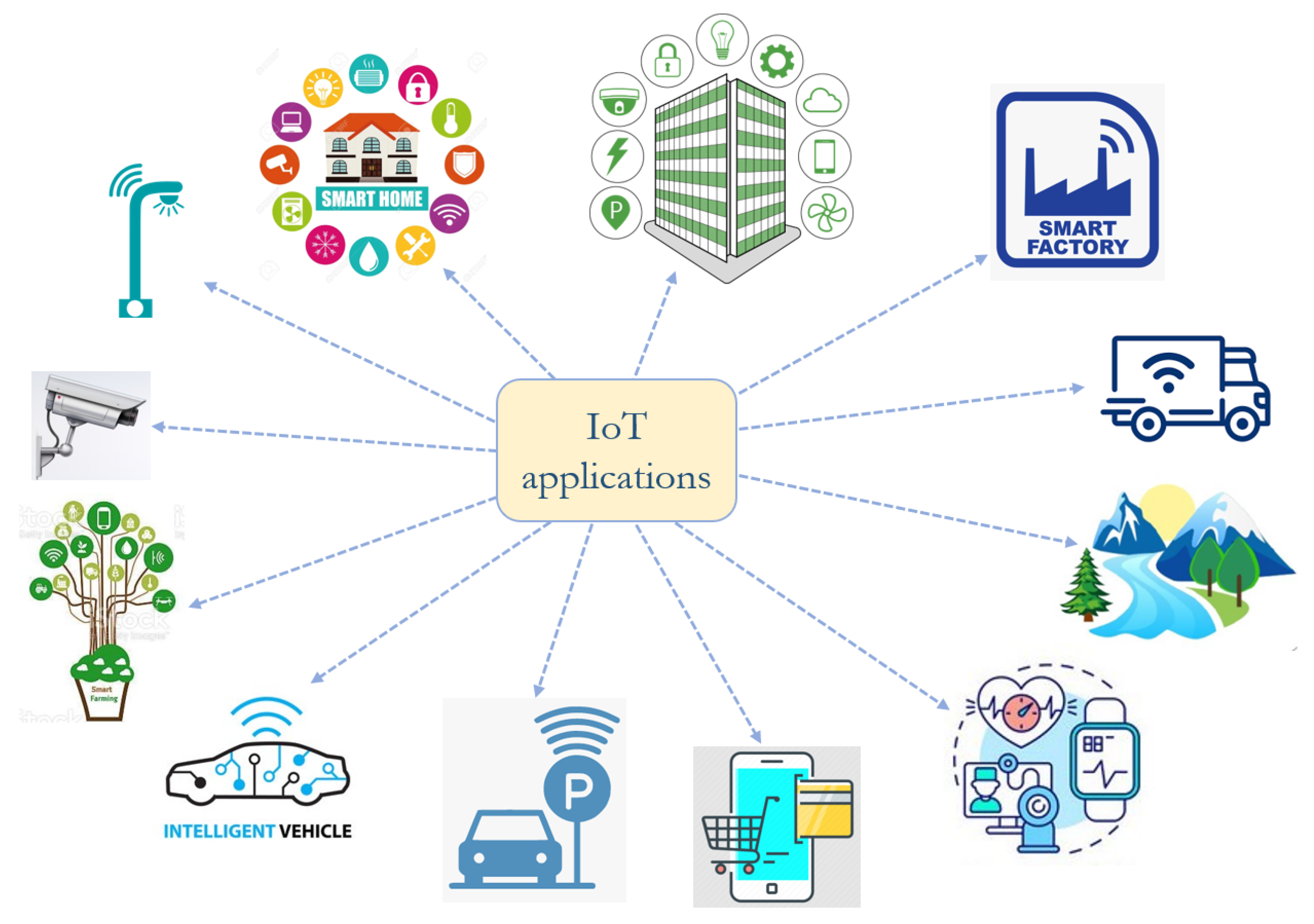
Let's explore some specific applications and illustrate their power. Consider the following examples:
Smart Agriculture: Imagine a vast agricultural expanse equipped with sensors that monitor soil moisture, temperature, and nutrient levels. Through remote access, a farmer can analyze this data from a smartphone or computer, make informed decisions about irrigation schedules, fertilizer application, and pest control, ultimately boosting crop yields and reducing resource waste. This remote capability extends beyond simply reading data; the farmer could also remotely control irrigation systems or even autonomous agricultural robots.
Industrial Automation: Factories and manufacturing plants are prime beneficiaries of remote access. Technicians can remotely diagnose and troubleshoot machinery malfunctions, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. Software updates can be pushed to devices without requiring on-site visits, improving operational efficiency. Furthermore, in cases where equipment spans across multiple locations, remote access provides a centralized management system for optimizing performance and reducing operational costs.
Healthcare: Remote patient monitoring systems allow healthcare professionals to track vital signs, such as heart rate and blood pressure, from a distance. This is especially beneficial for patients with chronic conditions, as it enables early detection of potential health issues and allows for proactive intervention. Remote access is also utilized in the operation of advanced medical devices, allowing specialists to perform procedures, even from remote locations, and provide real-time guidance during surgeries.
Smart Homes: Remote access is a cornerstone of the smart home experience. Homeowners can control lighting, climate control systems, security systems, and appliances from their smartphones, no matter where they are. This offers convenience and security, allowing them to monitor their homes and respond to events like potential intrusion or environmental emergencies. The ability to remotely adjust thermostats, for example, provides significant energy savings.
Energy Management: Smart grids utilize remote access to monitor and control energy distribution, optimising supply and demand. Utilities can remotely manage smart meters, detect outages, and optimize the flow of electricity, making the power grid more reliable and efficient. This leads to reduced energy waste and improved sustainability.
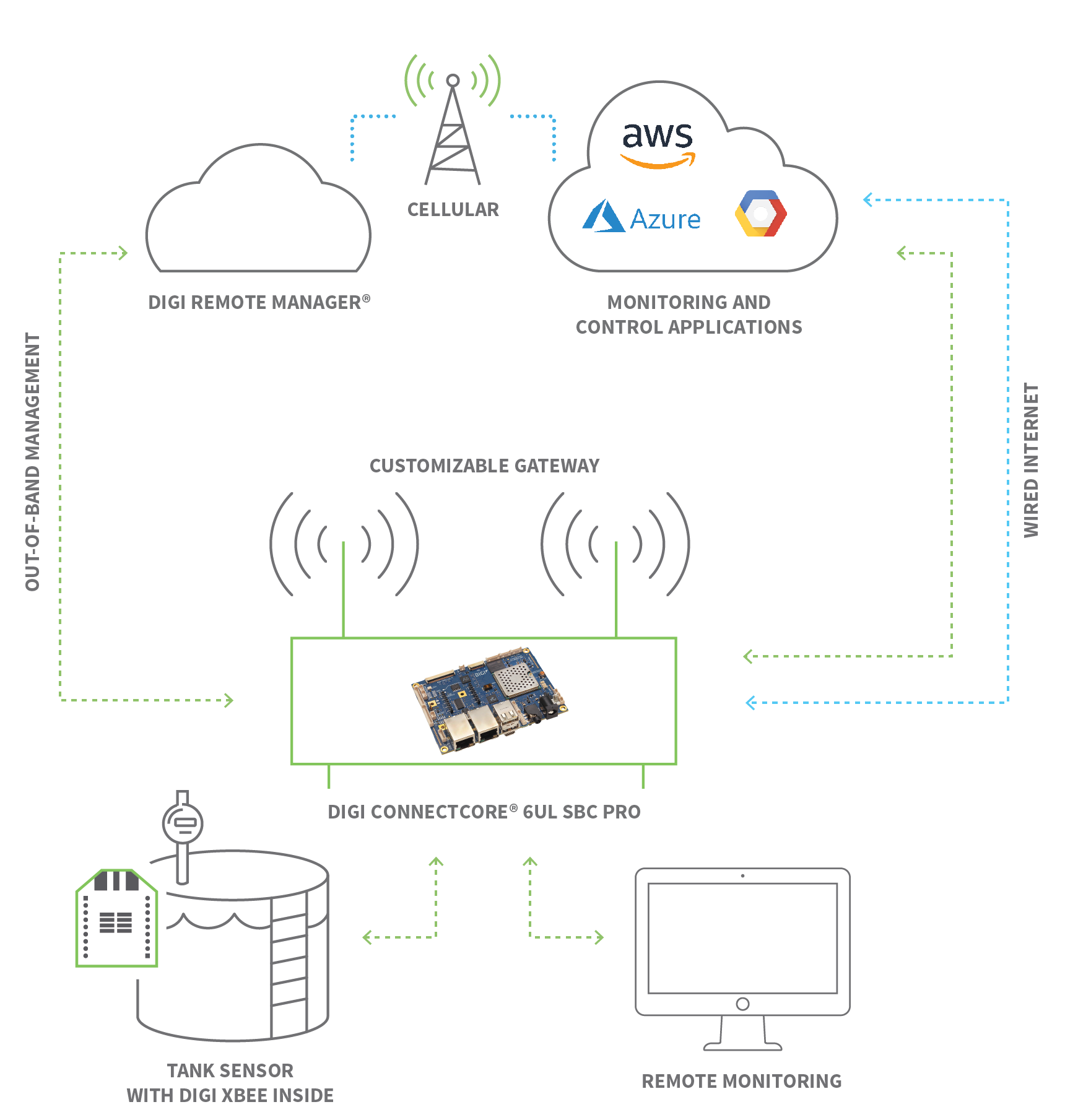
Remote Access Technologies: Implementing remote access in IoT ecosystems involves a combination of hardware and software. IoT devices are typically connected to a network via Wi-Fi, cellular, or other communication protocols. These devices then send their data to cloud platforms or local servers, which enable remote monitoring and control. Security is paramount in this type of setup, requiring encryption, authentication, and other security measures to protect against unauthorized access and cyber threats.
Here is a more detailed look at the technologies that allow remote access to be achieved in the IoT world:
Cloud Computing: Cloud platforms are central to remote access IoT deployments, serving as hubs for data storage, processing, and device management. They provide scalability, allowing businesses to manage vast numbers of connected devices efficiently. Examples include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform.
IoT Gateways: Acting as intermediaries between devices and the cloud, IoT gateways aggregate data, perform edge computing, and provide a secure channel for remote access. They enhance security and enable local processing, minimizing latency and bandwidth usage.
Communication Protocols: Several protocols are commonly used for communication in remote access IoT systems, including MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) for lightweight messaging, CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol) for resource-constrained devices, and HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) for web-based communication.
Security Protocols: Ensuring secure remote access is crucial, and various security protocols are employed. These include Transport Layer Security (TLS) and Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) for encrypted communication, as well as authentication mechanisms like two-factor authentication and digital certificates.
Remote Access Tools: Software tools designed specifically for remote access and device management are also used. These include VPNs, remote desktop applications, and IoT platform-specific tools that offer secure access to connected devices for monitoring, control, and troubleshooting.
The benefits of remote access in IoT are numerous. Firstly, it leads to improved efficiency by allowing for the quick resolution of problems and streamlined operations. It minimizes the need for on-site maintenance, saving time and reducing costs. Secondly, remote access facilitates enhanced decision-making, by providing real-time data to help operators make informed decisions. Thirdly, the ability to remotely monitor and control devices increases safety, especially in hazardous environments. Finally, remote access enables better resource management, leading to reduced waste and improved sustainability.
However, remote access in IoT is not without its challenges. One of the primary concerns is security. As IoT devices become more connected, they are vulnerable to cyberattacks. Ensuring robust security measures, such as encryption and authentication, is critical to preventing unauthorized access and data breaches. Another challenge is the complexity of managing a large number of connected devices. Deploying and maintaining remote access solutions requires careful planning, configuration, and ongoing monitoring. Furthermore, bandwidth limitations can restrict the amount of data that can be transmitted, particularly in areas with limited connectivity. Also, ensuring compatibility across different devices and platforms can be a complex process.
The future of remote access in IoT is brimming with potential. Technological advancements, such as 5G networks, offer faster and more reliable connections, enabling a new generation of remote applications, particularly in areas like autonomous vehicles and advanced robotics. Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) will enable even smarter and more proactive remote management. This will allow systems to predict and prevent failures, optimize performance, and automate complex tasks. Moreover, the increasing use of edge computing will bring processing power closer to the devices, improving response times and reducing bandwidth requirements. The evolution of these technologies suggests a future where remote access becomes even more seamless, secure, and essential to the way we live and work.
The Road Ahead: Remote access is more than a technological feature; it's a fundamental shift in how we interact with the world around us. As IoT deployments become more sophisticated and interconnected, the role of remote access will continue to grow, pushing boundaries and transforming industries. Staying ahead of the curve means prioritizing security, embracing innovation, and focusing on user-centric design. As the technology advances and the IoT expands, the ability to access and control devices from a distance will not just be a convenience; it will be a necessity.