Best Ways To Remotely Manage IoT Over Internet (+Tips)
Is the seamless control and efficient management of Internet of Things (IoT) devices across vast geographical distances truly within reach? The capacity to remotely manage IoT devices over the internet is not just a technological possibility; it's becoming an operational necessity, reshaping industries and redefining the very nature of connectivity.
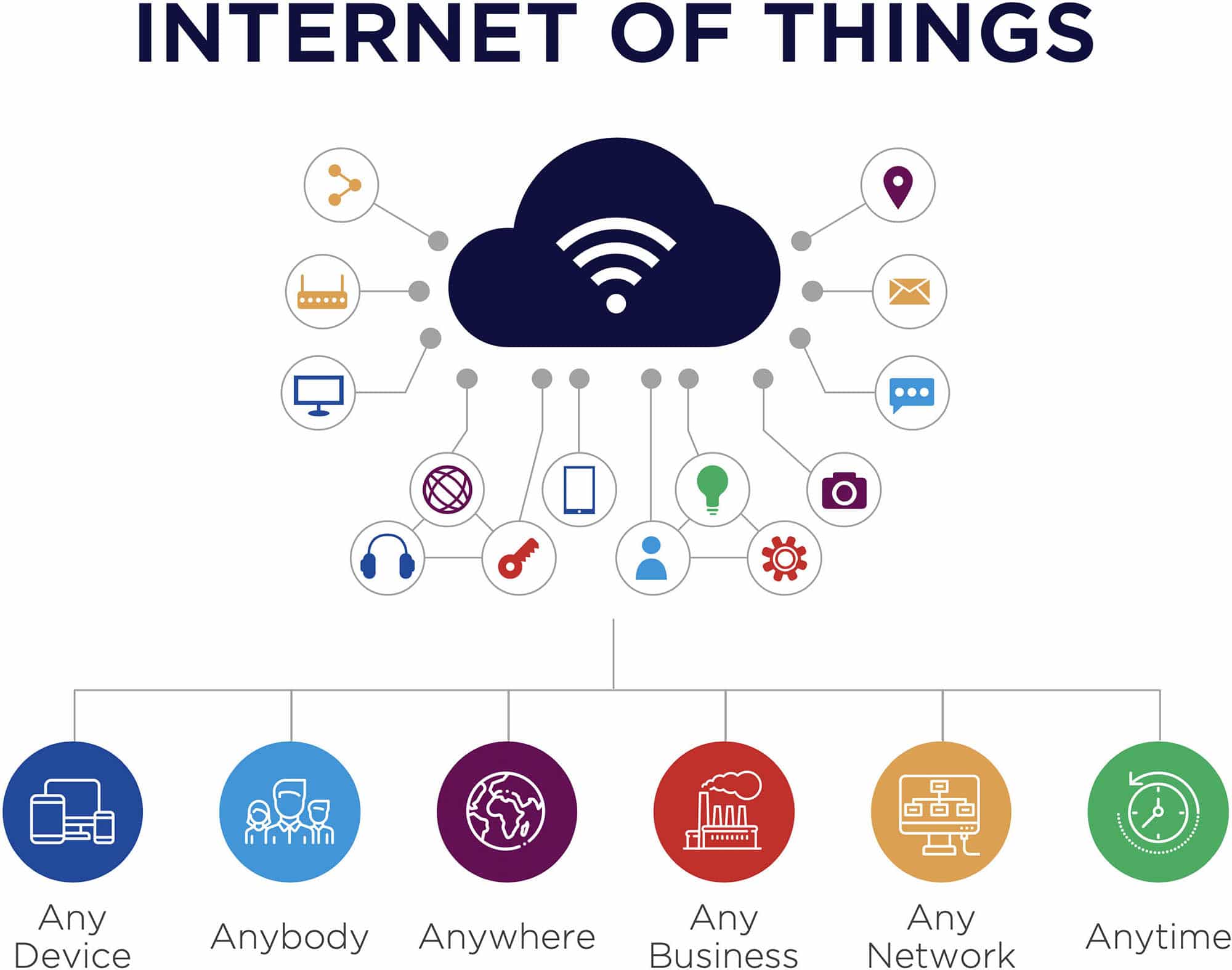
The rapid proliferation of IoT devices, from smart home appliances and industrial sensors to sophisticated medical equipment and environmental monitoring systems, has created an unprecedented need for robust and efficient remote management solutions. These devices, often deployed in remote or inaccessible locations, generate vast amounts of data and require constant monitoring, maintenance, and updates. The traditional methods of on-site visits for configuration, troubleshooting, and software updates are simply not scalable or cost-effective in the face of such exponential growth. Remote management, leveraging the power of the internet, offers a transformative approach, enabling organizations to oversee their IoT deployments with unparalleled efficiency and control.
The core of remote IoT management lies in the ability to establish secure and reliable communication channels between the central management platform and the individual devices. This typically involves the use of secure protocols, such as HTTPS and TLS, to encrypt data transmission and protect against unauthorized access. Device authentication and authorization mechanisms further enhance security, ensuring that only authorized users and devices can access and control the system. The underlying infrastructure for this communication often relies on a combination of technologies, including cellular networks, Wi-Fi, and satellite communication, depending on the location and connectivity requirements of the devices.
A well-designed remote management system provides a comprehensive suite of tools for device configuration, monitoring, and maintenance. This includes the ability to remotely configure device settings, update firmware and software, monitor device performance, and troubleshoot issues. Real-time monitoring dashboards provide a clear overview of device status, allowing administrators to quickly identify and respond to potential problems. Automated alerts and notifications can be configured to trigger responses to specific events, such as device failures or performance degradation, minimizing downtime and ensuring optimal device operation.
The benefits of remote IoT management are numerous and far-reaching. By eliminating the need for on-site visits, organizations can significantly reduce operational costs, save time, and improve efficiency. Centralized management platforms provide a single point of control for all devices, simplifying the management process and improving visibility across the entire IoT deployment. Remote access also enables organizations to provide faster and more effective support, allowing technicians to diagnose and resolve issues quickly, even in geographically dispersed locations. Furthermore, remote management facilitates the deployment of over-the-air (OTA) updates, enabling organizations to push new features, bug fixes, and security patches to devices without requiring physical access, ensuring that devices remain up-to-date and secure.
The choice of remote management platform and tools is crucial for the success of any IoT deployment. Several factors should be considered when selecting a solution, including the specific requirements of the application, the type of devices being managed, and the desired level of security and scalability. Many platforms offer a range of features and capabilities, from basic device monitoring to advanced analytics and predictive maintenance. Some also provide integration with other enterprise systems, such as customer relationship management (CRM) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, enabling organizations to gain a more holistic view of their IoT data.
Here's a look at the key components and functionalities involved in implementing and utilizing effective remote IoT management strategies, examining the essential building blocks that empower organizations to oversee their IoT deployments efficiently:
1. Secure Connectivity: The foundation of remote IoT management lies in secure and reliable communication channels. This involves establishing secure connections between the central management platform and the individual IoT devices. This can be achieved through various protocols and technologies. Secure protocols such as HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) and TLS (Transport Layer Security) are employed to encrypt data transmission, safeguarding sensitive information from unauthorized access during transit. Device authentication and authorization mechanisms are crucial for verifying the identity of devices and ensuring that only authorized entities can access and control the system. This is usually achieved using digital certificates, unique identifiers, and robust password policies. This ensures only legitimate devices can communicate with the management platform. The choice of connectivity options often depends on the deployment environment and device capabilities. Cellular networks (4G, 5G) provide wide coverage, while Wi-Fi offers high bandwidth within limited areas. Satellite communication becomes essential for devices in remote locations where other options are unavailable. The implementation of Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) adds an extra layer of security by creating encrypted tunnels for communication over public networks.
2. Device Management Platform: A robust device management platform serves as the central hub for monitoring, configuring, and maintaining IoT devices. This platform provides a comprehensive interface for administrators to manage the entire lifecycle of their devices. Key functionalities include device onboarding and provisioning, where new devices are securely registered and configured to connect to the network. Remote configuration allows administrators to adjust device settings, such as network parameters, sensor configurations, and operational modes, from a central location. Over-the-air (OTA) updates enable the seamless deployment of firmware and software updates to keep devices up-to-date with the latest features, security patches, and bug fixes. Device monitoring tools provide real-time insights into device health, performance metrics, and operational status. Alerts and notifications can be configured to trigger actions based on specific events or thresholds, such as device failures, performance degradation, or security breaches. The platform should also support data analytics and reporting features to help organizations analyze device data, identify trends, and optimize their IoT deployments.
3. Data Collection and Processing: IoT devices generate vast amounts of data, and effective remote management requires a system for collecting, processing, and analyzing this information. Data collection methods vary depending on the device and the application. Sensors embedded in IoT devices capture data such as temperature, pressure, location, and other relevant parameters. Data transmission protocols, such as MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) and CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol), are used to transmit data from devices to the management platform or a data storage system. Data processing involves cleaning, transforming, and aggregating the collected data to extract meaningful insights. This can involve filtering out irrelevant data, converting data formats, and performing calculations to derive key performance indicators (KPIs). Data analytics tools provide the capability to visualize data, identify trends, and detect anomalies. Machine learning algorithms can be used to predict device failures, optimize performance, and identify opportunities for improvement.
4. Security Measures: Security is paramount in remote IoT management, as devices are often vulnerable to cyberattacks. A multi-layered security approach is crucial to protect devices and data from unauthorized access, data breaches, and malicious activity. Strong authentication and authorization mechanisms are essential to verify the identity of devices and users. Encryption techniques, such as TLS and AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), are used to protect data in transit and at rest. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are conducted to identify and address potential security weaknesses. Device hardening involves configuring devices to minimize their attack surface by disabling unnecessary features and services. Security monitoring tools continuously monitor device activity for suspicious behavior or security breaches. The implementation of intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS) helps to detect and mitigate potential threats. Security best practices, such as using strong passwords, regularly updating firmware and software, and isolating devices from the broader network, are crucial for maintaining a secure IoT environment.
5. Remote Troubleshooting and Diagnostics: Remote management systems offer tools for diagnosing and resolving issues with IoT devices without requiring physical access. Remote access capabilities enable technicians to connect to devices remotely to troubleshoot problems. Diagnostic tools provide insights into device logs, error messages, and system configurations. Remote debugging tools allow technicians to step through code, identify the root cause of errors, and test fixes. Over-the-air (OTA) updates can be used to deploy software patches or firmware updates to resolve issues. The use of remote diagnostic tools significantly reduces downtime, accelerates problem resolution, and minimizes the need for costly on-site visits.
6. Scalability and Integration: IoT deployments can range from a few devices to thousands or even millions. Remote management platforms must be scalable to accommodate growth. Scalability is achieved through various techniques, such as using cloud-based infrastructure, distributing workloads across multiple servers, and employing efficient data storage and processing solutions. Integration capabilities are essential to connect the remote management platform with other enterprise systems, such as CRM, ERP, and asset management systems. This enables organizations to gain a holistic view of their IoT data and integrate IoT data with other business processes. APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) allow the platform to integrate with other systems and applications. The use of industry standards and open protocols promotes interoperability and facilitates seamless data exchange.
The impact of remote management extends far beyond simple convenience. It enables predictive maintenance strategies, where data analysis is used to anticipate device failures and schedule maintenance proactively, minimizing downtime and extending the lifespan of devices. This is particularly valuable in industrial settings, where even brief periods of downtime can result in significant financial losses. Furthermore, the ability to remotely monitor and control devices allows for the optimization of energy consumption, leading to cost savings and reduced environmental impact. Smart agriculture, for example, utilizes remote sensors and control systems to optimize irrigation and fertilization, maximizing yields while conserving resources. This efficiency is replicated in various sectors, highlighting the versatility and adaptability of remote IoT management.
However, the implementation of remote IoT management is not without its challenges. Security is a paramount concern, and organizations must adopt a multi-layered approach to protect devices and data from cyber threats. This includes the use of robust authentication and authorization mechanisms, encryption techniques, and regular security audits. The complexity of managing a large and diverse network of devices can also be a challenge. Organizations must carefully select the right platform and tools to meet their specific needs and ensure that they have the necessary expertise to manage and maintain the system effectively. The integration of IoT devices with existing IT infrastructure can also present challenges, requiring careful planning and coordination. The cost of implementing remote management solutions can also be a factor, especially for large-scale deployments. However, the long-term benefits, such as reduced operational costs, improved efficiency, and enhanced security, often outweigh the initial investment.
The future of remote IoT management is bright, with significant advancements expected in several areas. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) will play an increasingly important role in automating tasks, improving device performance, and predicting potential failures. Edge computing, where data processing and analysis are performed closer to the devices, will improve responsiveness and reduce latency. The adoption of 5G and other advanced communication technologies will provide faster and more reliable connectivity. The development of new standards and protocols will enhance interoperability and facilitate the integration of IoT devices with other systems. The emergence of new business models, such as device-as-a-service (DaaS), will enable organizations to adopt remote management solutions more easily and cost-effectively.
The evolution of remote IoT management reflects a broader shift towards a more connected and intelligent world. As the number of IoT devices continues to grow, the need for robust and efficient remote management solutions will only increase. Organizations that embrace remote management will be better positioned to capitalize on the benefits of IoT, improve their operational efficiency, and gain a competitive advantage. The convergence of advanced technologies, such as AI, edge computing, and 5G, will further enhance the capabilities of remote IoT management, enabling organizations to optimize their IoT deployments and unlock new levels of efficiency and innovation. The possibilities are vast, and the future of remote IoT management is poised to transform industries and reshape the way we interact with the world around us.
In the realm of "remote manage iot over internet," the following table provides an overview of key benefits:
| Benefit Category | Specific Advantages | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Operational Efficiency | Reduced on-site visits, centralized management, automation of tasks | Lower operational costs, faster response times, improved resource allocation |
| Enhanced Security | Secure communication protocols, remote patching and updates, device authentication | Reduced risk of security breaches, improved device protection, compliance with regulations |
| Cost Savings | Reduced travel expenses, predictive maintenance, energy optimization | Lower operating costs, increased asset lifespan, improved sustainability |
| Scalability | Cloud-based infrastructure, support for large deployments, adaptable to changing needs | Accommodates growth, enables future expansion, facilitates long-term planning |
| Data-Driven Insights | Real-time monitoring, data analytics, predictive maintenance | Improved decision-making, proactive issue resolution, optimized device performance |
| Improved Customer Experience | Faster support, remote troubleshooting, proactive issue resolution | Increased customer satisfaction, improved service delivery, enhanced brand reputation |