RemoteIoT: Use It Without Router Worries (Step-by-Step)
Can you truly harness the power of the Internet of Things (IoT) from anywhere, even when shielded by the complexities of a home or office router? The answer, unequivocally, is yes. The ability to use remote IoT devices behind a router without directly exposing them to the public internet is a critical aspect of modern IoT deployment, ensuring security and accessibility. This capability unlocks a universe of possibilities, from smart home automation and industrial monitoring to precision agriculture and remote healthcare, all while safeguarding your devices from unwanted intrusion. The challenge, however, lies in understanding the mechanics and implementing the correct strategies.
The modern digital landscape is a tapestry woven with layers of interconnected devices, each a potential point of access. Routers, acting as gatekeepers, provide crucial protection by employing Network Address Translation (NAT), essentially hiding devices behind a single public IP address. While this enhances security, it also presents a hurdle for remote access. Directly connecting to a device hidden behind NAT is akin to trying to reach a specific apartment building without knowing the complex address scheme of the building itself. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide, demystifying the methods and technologies that enable you to use remote IoT devices behind a router without compromising their integrity or ease of access. We'll explore the intricacies of port forwarding, VPNs, cloud-based solutions, and other innovative approaches, equipping you with the knowledge to securely connect and control your IoT ecosystem from any corner of the globe.
This exploration will encompass various techniques, but before diving into the specifics, it's important to understand the foundational principles. Think of your home network as a walled garden. Your router is the gate, protecting the precious flowers (your IoT devices) from the harsh elements (the open internet). Without the proper mechanisms, accessing those flowers remotely becomes an impossible task. We will provide several methods, each with its own strengths and weaknesses, to open the gate and allow controlled access to your devices.
To further illustrate the challenges and solutions, let's consider the case of a hypothetical smart home enthusiast, Alex. Alex wants to monitor the temperature in his greenhouse, control his sprinklers, and view live video feeds from security cameras, all while he's away on vacation. His devices are all connected to his home network, behind his router. Without proper configuration, he is essentially locked out of his system. We will look into the steps Alex should take to accomplish this.
Before delving into the technical aspects, it's crucial to understand the fundamental security considerations. Any method that allows remote access to your devices introduces potential vulnerabilities. Always prioritize strong passwords, regularly update firmware on your router and IoT devices, and implement firewalls to minimize the attack surface. Consider the potential impact of a security breach. What data is being collected and transmitted? What are the risks associated with unauthorized access? A proactive approach to security is not merely an option, but an absolute necessity.
Let's begin with the most straightforward, yet often misunderstood, method: Port Forwarding.
Port Forwarding: The Direct Approach
Port forwarding is the digital equivalent of building a direct bridge from the outside world to a specific device within your home network. It works by configuring your router to listen for incoming traffic on a specific port (a virtual "door") and then redirect that traffic to the designated device's internal IP address and port. For example, if Alex's security camera is running on port 8080 on his internal IP address 192.168.1.100, he could configure his router to forward incoming traffic on port 8080 to that specific internal address. Now, when Alex attempts to access his camera from outside the network, he would simply enter his public IP address followed by the port number (e.g., 123.456.78.90:8080) in his web browser. The router, upon receiving the request on port 8080, would forward it to the camera.
While seemingly simple, port forwarding has significant drawbacks. It requires a static public IP address, or the use of a Dynamic DNS service to keep track of a changing IP address. Moreover, it directly exposes your IoT devices to the internet, increasing the risk of unauthorized access. Every port you forward represents a potential entry point for hackers. The ease of setup must be weighed against the potential security vulnerabilities.
Port Forwarding: The Steps
The process of setting up port forwarding typically involves accessing your router's configuration interface through a web browser. You will need to know your router's IP address, which is often 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1, but can vary. Consult your router's manual for specific instructions. Once logged in, you will navigate to the port forwarding or virtual server section. Here, you will specify the following information:
- Service Name: A descriptive name for the port forwarding rule (e.g., "Security Camera").
- Protocol: The protocol used by the device (usually TCP, UDP, or both).
- External Port: The port number you want to use for external access (e.g., 8080).
- Internal Port: The port number the device is using internally (e.g., 8080).
- Internal IP Address: The internal IP address of the IoT device (e.g., 192.168.1.100).
After saving the settings, you should be able to access your device from outside your network using your public IP address and the external port. However, as stated before, this opens the door to potential security issues and is generally not recommended for sensitive devices.
VPN: A More Secure Approach
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) offer a more secure and versatile solution. A VPN creates an encrypted tunnel between your device and your home network, effectively placing you inside the network, allowing you to access your IoT devices as if you were physically present. Think of it as a secure underground passage bypassing the dangers of the open internet.
There are several ways to set up a VPN for remote access. The simplest method involves using a VPN service, where a third-party provider manages the VPN server and infrastructure. This is generally the easiest option, requiring minimal technical expertise, but comes with a subscription fee and raises the question of entrusting your traffic to a third party. VPN providers often offer applications that can be installed on your laptop, phone, or tablet that makes connecting to your home network simple.
Alternatively, you can set up your own VPN server on your router or on a separate device within your home network. This option provides greater control over your data and privacy, as you're not reliant on a third-party provider. However, it requires more technical knowledge and configuration.
To set up a VPN on your router, your router needs to support this functionality, which many modern routers do. Check your router's manual to see if it supports VPN server functionality, typically either PPTP, L2TP/IPsec, or OpenVPN. OpenVPN is considered the most secure protocol. Once enabled, you will need to configure the VPN server with a username, password, and encryption settings. You will then need to install a VPN client on your remote device, such as your smartphone, and configure it with the necessary server address, username, and password. When you connect to the VPN, your device will be assigned an IP address within your home network, allowing you to access your IoT devices as if you were physically present.
Cloud-Based Solutions: Simplifying the Complexity
Cloud platforms are changing how we interact with our devices. Cloud platforms offer robust solutions for remote access, simplifying the complexities of port forwarding and VPN configuration. Many IoT device manufacturers offer cloud-based services that allow you to remotely access and control your devices through their platforms. These services often handle the complexities of network configuration and security, making it a more user-friendly approach.
These cloud-based services work by allowing your IoT devices to establish a connection to a server in the cloud. Your devices periodically send data to the cloud server, and you can then access and control your devices through a web browser or mobile app. This eliminates the need for port forwarding or VPNs, as you are connecting to the cloud service, not directly to the devices themselves.
The advantage is that they often include features like device management, data storage, and analytics, making them a comprehensive solution for your IoT needs. The disadvantages include the reliance on a third-party service, which means your data is stored and processed by someone else. There could also be subscription costs associated with these cloud services. Also, you need to carefully evaluate the privacy policies and security practices of the cloud provider before entrusting them with your data.
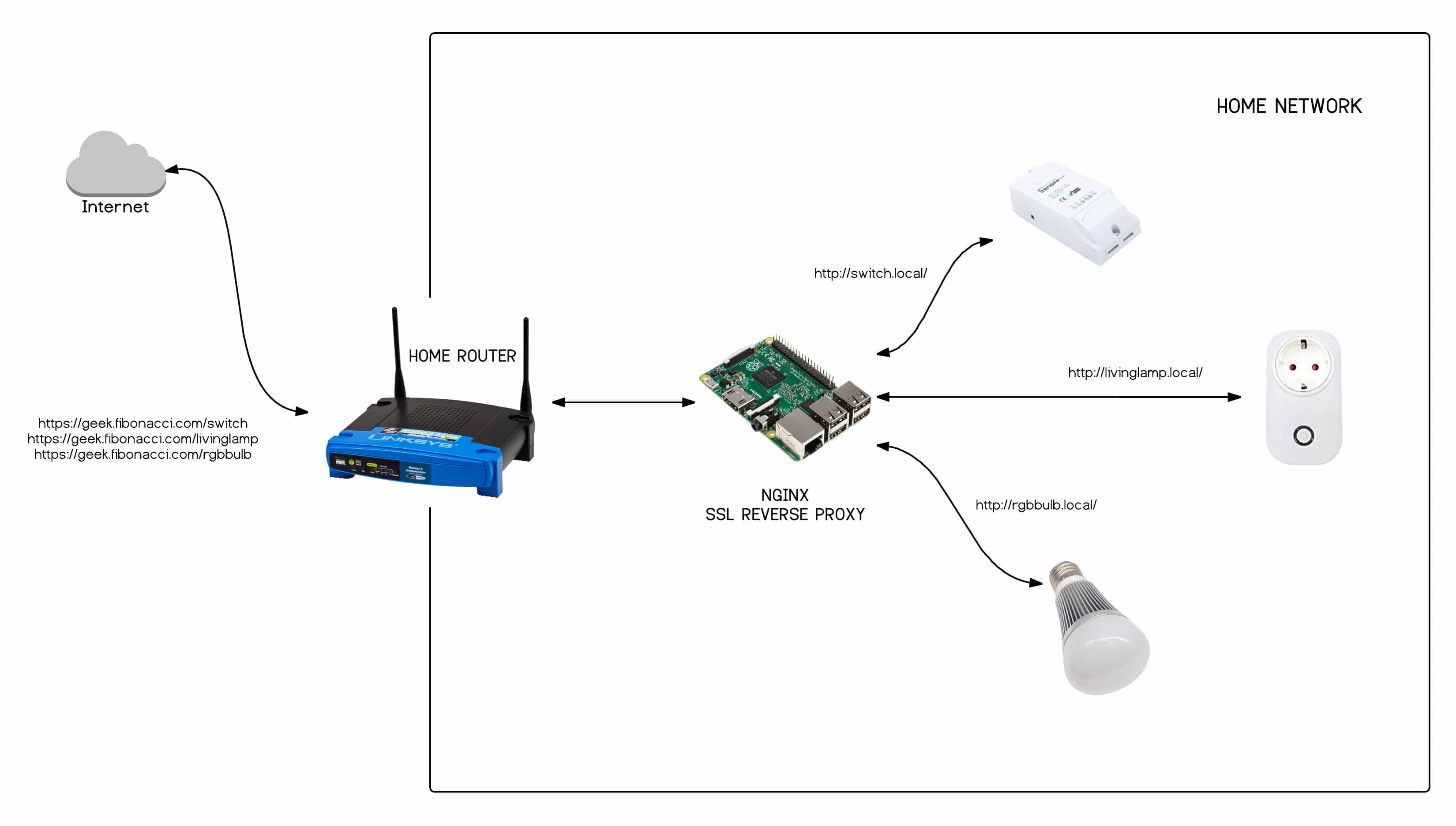
Reverse Proxy: A Powerful Alternative
A reverse proxy acts as an intermediary between the internet and your internal network. It receives incoming requests and forwards them to the appropriate internal server. This approach has several advantages, including enhanced security, load balancing, and SSL encryption.
To implement a reverse proxy, you will need a server, either physical or virtual, that is accessible from the internet. Popular software options include Nginx and Apache, which can be configured to act as a reverse proxy. You will configure the reverse proxy to listen for incoming traffic on a specific port (e.g., 80 or 443), and then forward that traffic to the internal IP address and port of your IoT devices. When a request comes in, the reverse proxy will examine the request, apply any necessary security checks, and forward the request to the appropriate device.
This approach provides an extra layer of security, as the reverse proxy can be configured to filter malicious traffic and protect your internal network from direct exposure. It can also handle SSL encryption, adding an extra layer of security for data transmitted between the client and the reverse proxy. This is useful when you want to protect your devices by using HTTPS protocol.
IoT Gateways: The Intelligent Hub
IoT gateways are dedicated devices designed to connect and manage multiple IoT devices. They act as a central hub, handling communication protocols, data processing, and security. They often offer built-in features for remote access, making them a straightforward solution.
An IoT gateway sits within your local network, connecting to your IoT devices via various protocols like Zigbee, Z-Wave, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth. It then connects to the internet, allowing you to access your devices remotely. Many IoT gateways have a built-in web interface or mobile app that allows you to view and control your devices. They also provide features like data logging, device management, and security.
IoT gateways simplify the process of connecting and managing IoT devices, especially in complex deployments. The gateway handles the intricacies of network communication and protocol conversion, offering a user-friendly interface for remote access and control. It can also act as a security buffer, protecting your internal network from direct exposure.
Security Considerations: A Never-Ending Vigil
No matter which method you choose, security should always be your top priority. The following are essential considerations for securing your IoT devices and remote access:
- Strong Passwords: Use strong, unique passwords for all your devices and accounts. Avoid using default passwords.
- Regular Updates: Keep your router's firmware and the firmware of your IoT devices updated to patch security vulnerabilities.
- Firewall: Enable the firewall on your router and IoT devices to block unauthorized access.
- Encryption: Use encryption to protect data transmission. For example, use HTTPS for web access.
- Network Segmentation: Consider isolating your IoT devices on a separate network or VLAN to limit the impact of a security breach.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Enable 2FA wherever possible to add an extra layer of security.
- Monitor Your Network: Monitor your network traffic for suspicious activity.
- Review Logs: Regularly review logs on your router and IoT devices to detect potential security breaches.
By consistently applying these security measures, you can minimize the risks associated with remote access and protect your IoT devices from unauthorized access.
Choosing the Right Method: A Tailored Approach
The best method to use remote IoT devices behind your router without depends on your specific needs, technical expertise, and security requirements. Consider the following factors when making your decision:
- Technical Expertise: Some methods, such as setting up a VPN server or a reverse proxy, require more technical knowledge than others.
- Security Requirements: If security is your primary concern, consider using a VPN or a reverse proxy.
- Ease of Use: Cloud-based solutions and IoT gateways offer the easiest setup.
- Number of Devices: If you have a large number of devices, an IoT gateway might be the best choice.
- Budget: Some methods, such as cloud-based solutions, involve subscription costs.
The Future of Remote IoT: A World of Possibilities
As the Internet of Things continues to evolve, the methods for accessing and controlling devices remotely will also evolve. We can expect to see more sophisticated and user-friendly solutions that offer enhanced security and ease of use. AI-powered security systems may become the standard, autonomously detecting and mitigating potential threats. Device manufacturers will likely integrate remote access capabilities directly into their products, simplifying the setup process. The focus will always be on secure and reliable access to your devices from anywhere in the world.
The ability to securely use remote IoT devices behind a router without is a fundamental requirement in today's interconnected world. By understanding the available methods and implementing the appropriate security measures, you can unlock the full potential of your IoT devices, bringing smart home automation, industrial monitoring, and countless other innovations within your reach. The key is a blend of technical awareness and a proactive approach to security, which are vital in navigating the evolving digital landscape.