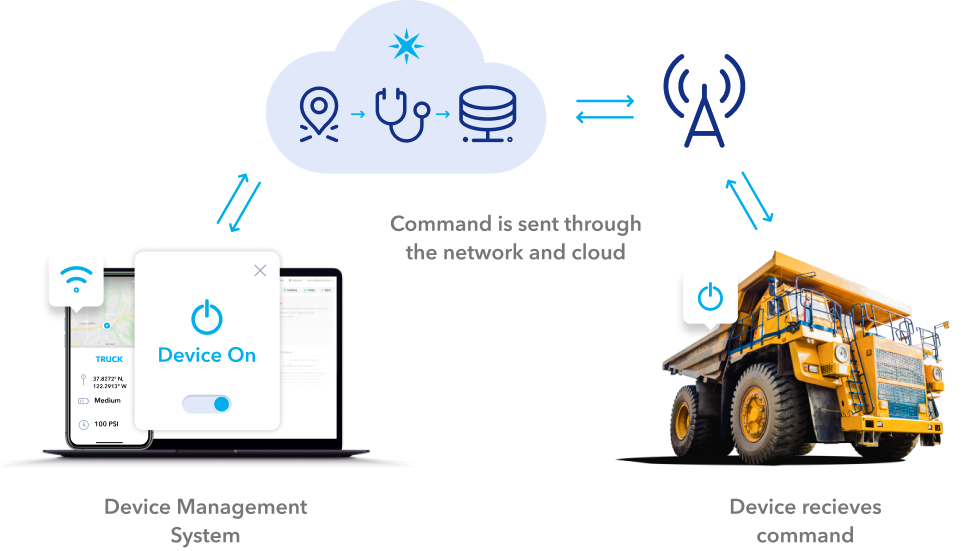
[How-To] Control Remote IoT Devices: Easy Guide!
Are we truly in control? The proliferation of "control remote IoT" devices has fundamentally altered the landscape of our lives, offering unprecedented convenience and connectivity, but simultaneously raising critical questions about security, privacy, and the very nature of control itself.
The phrase "control remote IoT" encapsulates a rapidly evolving field, a nexus where the physical world meets the digital, and where the ability to command and monitor devices from afar becomes commonplace. It's the thermostat adjusted from your phone, the lights dimmed with a voice command, the security system armed while you're miles away. This technology, while seemingly futuristic, is rapidly integrating into the everyday, shaping our homes, our cities, and even our bodies. The Internet of Things, once a buzzword, is now a pervasive reality. Yet, the seemingly effortless control provided by "control remote IoT" systems also opens up a Pandora's Box of potential vulnerabilities. The very features that make these devices appealing their remote accessibility and interconnectedness are also their greatest weaknesses, offering opportunities for malicious actors to exploit vulnerabilities and disrupt our lives.
Consider the implications of a smart home ecosystem. A homeowner might be able to control their lighting, heating, and security systems from their phone. But what happens when the network is compromised? Are they vulnerable to a cyberattack? The concept of "control remote IoT" extends far beyond the home. In the industrial sector, remote monitoring and control of machinery and equipment are becoming increasingly prevalent, enhancing efficiency and reducing operational costs. However, the potential impact of a cyber breach on critical infrastructure power grids, water treatment plants, and transportation networks cannot be overstated.
The evolution of "control remote IoT" is undeniably driven by the convergence of several key technological advancements. The continuous miniaturization of electronics has made it possible to embed sensors and communication modules into a vast array of objects. The increasing processing power of these embedded devices allows for sophisticated data collection and analysis. The wide availability of high-speed internet and wireless communication technologies, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular networks, ensures seamless connectivity. Furthermore, the proliferation of cloud computing platforms provides the necessary infrastructure for data storage, processing, and remote control capabilities. These combined elements have created the foundation for a digital ecosystem where almost anything can be connected and controlled remotely.
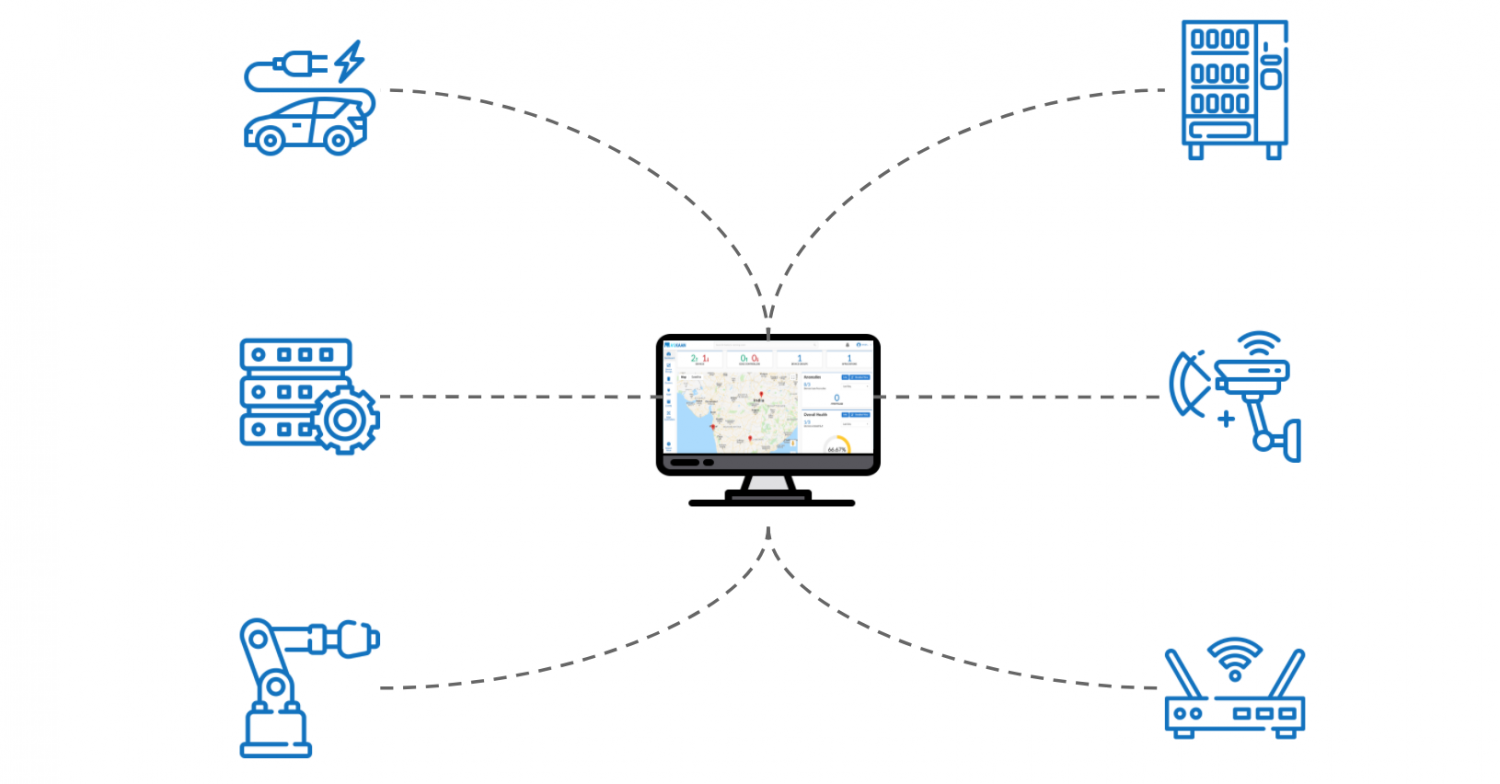
The applications of "control remote IoT" are incredibly diverse, spanning across many different industries and aspects of life. In the realm of healthcare, remote patient monitoring systems allow doctors to track vital signs and provide timely interventions. Smart medical devices, such as insulin pumps and pacemakers, can be controlled and monitored remotely. In the automotive industry, connected cars offer features like remote diagnostics, over-the-air software updates, and even self-parking capabilities. Smart agriculture utilizes sensors and remote control systems to monitor soil conditions, optimize irrigation, and manage farm equipment, leading to increased efficiency and productivity. In the retail sector, smart shelves and inventory management systems track products in real-time, providing valuable data about customer behavior and supply chain logistics. The applications are expanding continuously, reflecting the underlying technological progress.
The promise of "control remote IoT" is alluring. It promises to enhance convenience, improve efficiency, and offer new ways to interact with the world around us. However, we must also be prepared to navigate the complex challenges that come with this technological transformation. The rise of "control remote IoT" also creates significant legal and ethical considerations. Who is responsible when a smart device malfunctions and causes harm? How do we ensure that our data is protected from unauthorized access and misuse? What are the implications of mass surveillance and the erosion of privacy? These questions demand thoughtful consideration and proactive solutions.
Security is perhaps the most significant concern when it comes to "control remote IoT". The interconnected nature of these devices creates numerous attack vectors for cybercriminals. Many IoT devices have inherent security vulnerabilities, such as weak passwords, lack of encryption, and outdated software, which can be easily exploited. As the number of connected devices continues to grow, the potential for large-scale cyberattacks, such as botnet attacks and ransomware attacks, also increases. Robust security measures, including strong authentication protocols, regular software updates, and end-to-end encryption, are crucial for mitigating these risks. Furthermore, it's crucial to develop and implement industry-wide security standards and regulations to establish a minimum level of security for all "control remote IoT" devices. The security landscape evolves continuously, calling for adaptive security strategies.
Privacy is another significant concern in the age of "control remote IoT." Many devices collect vast amounts of personal data, which can be used to track our behavior, monitor our activities, and even infer our personal preferences. This data can be vulnerable to breaches, misused by companies, or exploited for marketing or surveillance purposes. Data privacy regulations, like GDPR and CCPA, attempt to address some of these concerns. However, the effective enforcement of these regulations and the development of robust data privacy practices are critical to protecting individuals' privacy. Furthermore, users need to be aware of the data that their devices collect and how that data is used. Transparency and user control are essential elements in maintaining data privacy.
Looking ahead, we can expect to see even more innovative applications of "control remote IoT". The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) will enable more sophisticated control systems, allowing devices to learn from our behavior and adapt to our needs. The development of 5G networks and other advanced communication technologies will enhance connectivity and enable new applications, such as autonomous vehicles and smart cities. The expansion of edge computing will move processing closer to the devices, reducing latency and improving performance. "Control remote IoT" will continue to evolve and redefine the boundaries of what is possible, offering exciting new opportunities for innovation and progress.
The ethical considerations surrounding "control remote IoT" are equally important. As technology advances, we must consider the potential implications of these new capabilities. For instance, the use of AI-powered devices raises questions about algorithmic bias and the fairness of decision-making processes. The increasing reliance on automation can lead to job displacement and the erosion of human autonomy. The use of connected devices for surveillance and data collection can threaten civil liberties and human rights. It is essential to develop ethical guidelines and regulatory frameworks to ensure that the development and deployment of "control remote IoT" technologies are aligned with our values and principles.
Consider the concept of the smart home. A homeowner can control their lights, thermostat, security system, and entertainment systems remotely. They can even receive real-time alerts when unexpected activity is detected. However, this convenience comes with significant risks. The system is only as secure as its weakest link. Vulnerabilities in software or hardware can allow hackers to gain access to the system, compromising the homeowner's privacy and security. The potential consequences range from nuisance activities, such as turning lights on and off, to more severe breaches, like the theft of personal data or the unauthorized control of critical functions.
The industrial sector is also witnessing a significant shift towards "control remote IoT". Manufacturing plants are increasingly using remote monitoring and control systems to manage their production processes, monitor machinery, and optimize performance. This can lead to increased efficiency, reduced downtime, and lower costs. But if the systems are vulnerable to cyberattacks, the consequences could be catastrophic. Hackers could potentially disrupt production, damage equipment, or even gain access to sensitive intellectual property. Safeguarding these systems is therefore critical.
In the realm of transportation, "control remote IoT" is revolutionizing the way we get around. Connected cars are becoming increasingly common, offering features such as remote diagnostics, over-the-air software updates, and even autonomous driving capabilities. However, these advances also introduce new vulnerabilities. A successful hack of a vehicle's control system could potentially allow attackers to take control of the vehicle, potentially endangering the driver and passengers. This makes robust cybersecurity measures of paramount importance. The safety of self-driving cars also relies heavily on secure and reliable "control remote IoT" systems. These systems must make real-time decisions based on data from sensors, other vehicles, and infrastructure. Any disruption of these systems could have devastating consequences.
Agriculture is another key area for "control remote IoT". Precision agriculture utilizes sensors and remote control systems to monitor soil conditions, optimize irrigation, manage farm equipment, and streamline overall operations. The ability to remotely monitor and control these systems allows farmers to make data-driven decisions, leading to increased yields, reduced water consumption, and improved efficiency. If these systems are compromised, farmers might be unable to effectively manage their crops. This highlights the importance of securing these systems.
The "control remote IoT" landscape is characterized by rapid innovation and constant change. As more devices become connected, the potential for new applications and opportunities will continue to grow. To navigate this rapidly changing landscape, it is important to keep pace with new technologies, emerging threats, and evolving best practices. Furthermore, it's crucial to foster collaboration between industry, government, and academia to address the challenges and opportunities that "control remote IoT" presents. This collaboration should encompass the development of new security standards, the promotion of data privacy, and the establishment of ethical guidelines. Only with a multifaceted approach will we be able to realize the full potential of "control remote IoT" while mitigating the inherent risks.
The future of "control remote IoT" will depend on our ability to balance innovation with responsibility. We must embrace the benefits of these technologies while simultaneously addressing the risks they pose. This requires a proactive and collaborative approach, where security, privacy, and ethics are given equal weight. By prioritizing these critical areas, we can ensure that "control remote IoT" serves as a force for positive change, enhancing our lives and building a more connected, efficient, and sustainable future. The power of these technologies lies in our hands, and it's up to us to shape the future.